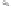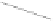Java Reference
In-Depth Information
Entry
u
←
5
repeat
if
r
then
v
←
A
v = 9
y = v+w
9
B
w = 5
if
p
then
u
←
6
x = v+w
else
w
←
5
x
←
v
+
w
else
y
←
v
+
w
u
←
7
repeat
if
q
then
C
z = v+w
z
←
v
+
w
83
until
r
v
←
2
v = 2
Exit
until
s
(a)
(b)
Figure 14.41: (a) A program; (b) Its control flow graph.
In this problem, an instruction a
ects the solution if it computes
v
+
w
or if it
changes the value of
v
or
w
, as follows:
ff
•
The Entry node of the program is assumed to contain an implicit com-
putation of
v
+
w
. For programs that initialize their variables,
v
+
w
is
certainly available after node Entry.Otherwise,
v
+
w
is uninitialized,
which allows the compiler to assume that the expression has
any
value
it chooses.
•
A node of the flow graph that computes the expression
v
+
w
makes
v
+
w
available on its outgoing edges.
•
A node of the flow graph that assigns
v
or
w
makes
v
+
w
unavailable.
We assume an assignment to
v
destroys the availability of
v
+
w
even if the
value of
v
is una
ff
ected by the assignment. For example, the assignment
v
=
v
+
0 does not really change
v
's value, but we leave the elimination
of such useless code to other optimization passes.
•
All other nodes have no e
ff
ect on the availability of
v
+
w
.