Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
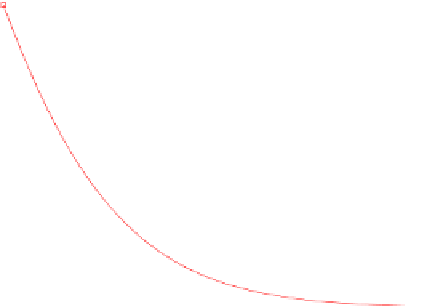
Fig. 6.1
Down-and-out,
down-and-in barrier put and
plain vanilla put option
Example 6.1.2
Consider a down-and-out and down-and-in put option. Set
K
=
100,
T
0
.
01. We plot the price of both options and the
corresponding plain vanilla put price in Fig.
6.1
. Here, we computed the down-
and-out barrier option using finite elements and applied formula (
6.1
) to obtain the
corresponding down-and-in contract.
=
1,
B
=
80,
σ
=
0
.
3 and
r
=
6.2 Asian Options
Asian options are path-dependent options where the payoff depends on the price
history of the underlying, in particular on the arithmetic average price at maturity,
T
1
S
T
:=
S(τ)
d
τ.
(6.3)
T
−
t
0
t
0
The term
T
−
t
0
denotes the length of the averaging period. Applying Itô's formula
we
set
t
0
=
0. There are different types of o
pt
ions. The
fixed strike
call has payoff
(S
T
−
K)
+
and the
floating strike
call
(S
−
S
T
)
+
. To derive the partial differential
equation, we introduce the
new variable
t
=
Y(t)
S(τ)
d
τ.
0
Since this history of the asset price is independent of the current price
S(t)
,
we
may treat S
,
Y and t as independent variables
. The value of an Asian can then be
obtained in the form
V(t,S,Y)
. We need a stochastic differential equation for the
vector process
(S, Y )
. Applying Itô formula, we obtain that
(S, Y )
is a diffusion
process,














































































































Search WWH ::

Custom Search