Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
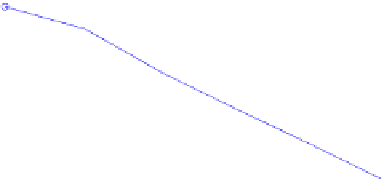
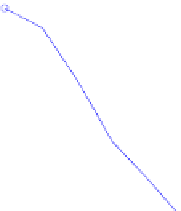
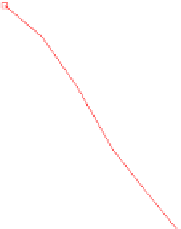
Fig. 15.2
Convergence rate
of the one-factor (
top
)and
two-factor (
bottom
) Bates
model on sparse tensor
product space
15.5 Further Reading
A stochastic volatility model with jumps comparable to the BNS model is the so-
called COGARCH(1
,
1) process introduced by Klüppelberg et al. [105]. This model
is a continuous time version of the popular GARCH model in discrete time and
states that the asset log-price
X
is given by d
X
t
=
σ
t
d
L
t
, where
L
is a Lévy pro-
cess and the jumps
L
of this Lévy process are also used to define the volatility
process
σ
. The model is generalized to the COGARCH(
p,q
) process by Brockwell
et al. [30].
A large class of stochastic volatility models is described by Carr et al. [37] where
the stock price process
S
is given as the ordinary or the stochastic exponential of a
stochastic volatility process
Z
t
=
L
Y
t
, which is obtained by subordinating a Lévy
process
L
to
Y
(which, for example, is given by the CIR model).

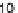




















































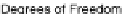

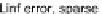

















































































































































































































































































































































































Search WWH ::

Custom Search