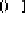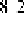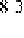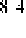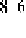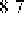Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
of
O
i
(1 ≤
i
≤
k
) should be chosen evenly in [0, 1), so that all rates can be assorted to
one nearest state
O
i
. Then we get a state transition matrix whose scale is
k
×
k
.
An example is given. Suppose we have
n
= 128 packets in one block, then the data
packet sequence can be donated as
P
0
P
1
…
P
127
. And at the clients, the correctly re-
ceived ones are signed as 1 and the others are signed as 0. Then the packet error rates
Q
j
s (
Q
j
=
N
0
/
n
,
N
0
presents the number of
P
0~
n
-1
= 0 in the
j
-th sequence) can be giv-
en. Here we set the scale
k
= 8 and the
O
i
s of the transition matrix are 0, 1/8,…, 7/8
(chosen evenly in [0, 1)). If the adjacent two packet error rates
Q
and
Q
′ got from the
feedback strings are 75/128 and 23/128, they will be respectively assorted to the near-
est states
O
6
= 5/8 and
O
2
= 1/8. Then the count
a
62
in the matrix should plus 1. So we
fill the transition matrix as (2) after all the rates are assorted to the nearest
O
i
in one
experiment. After that, it will search the matrix according to the following rate
Q
A
,
assumed to be assorted to state
O
7
, to find out the maximum probability
a
7
Max
=
a
74
to
reach the next state
O
4
=
Q
B
. Then
Q
B
is the estimate the Markov chain model made.
(2)
So in this way, we can estimate the incoming possible packet error rate according to
the feedback values. All the probability values
a
ij
(1 ≤
i
,
j
≤
k
) in the state transition
matrix should be got from a mass of feedback values in one period and are believable.
3.3
The Adaptive Multicast Data Origin Authentication Model
In our model, we set three kinds of end as the server, the adversary and the clients.
The network model is set as Fig. 3. The server broadcasts messages to the heteroge-
neous clients and then the chosen clients will respond the bit strings which represent
whether the packets received correctly or not as well as the time delay messages. The
adversary could control parts of the network and attack the data packets on the way.
At the server, firstly some initial parameters are determined: the encoding parame-
ters
n
(
n
= 2
p
,
p
is a positive integer) and
m
(
m
<
n
), a set of
k
values of packet error
rate
O
i
(0
≤
O
i
<
1, 1
≤
i
≤
n
) as the coordinates of the transition matrix, and then
three threshold values, the time delay threshold value
t
, the limit time
t
0
and the pack-
et error rate threshold value
β
(0
< β < 1
). The same parameters are shared at the
clients too.
Secondly, the server starts to broadcast the message packets and the authentication
messages encoded by the IDA and the Merkle HASH tree as Fig. 2 with the initial
parameters
n
and
m
. The clients would send feedback messages of the time delay and
packet error rate to the server.