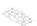Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
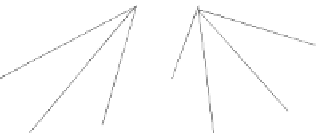
Fig. 3.
The multicast framework model
If the average decoding time in one period is beyond the threshold value
t
, the rep-
resentative clients will send the server a timeout label, and then the server will de-
crease the value of
n
as
n
=
n
/ 2. On the other hand, if the average time delay keeps
under the threshold value
t
for
t
0
time, then the server recovers the size
n
as
n
=
n
×
2.
And if the packet error rate is beyond the threshold value
β
, for example, the lost
packets and the forged packets from the adversary are altogether
ω
in a block of
n
packets, and
ω
/
n
> β
, then the representative clients will send the server the packet
sequence bit strings
P
1
P
2
…
P
n
. And the state transition matrix can be filled up using
our protocol as (1).
Next the server will estimate the incoming packet error rate according to the state
transition matrix. It will get a maximum probability to reach the next state
O
with the
last received rate, and the rate
Q
=
O
is the result estimated by the Markov chain. At
the same time, after the messages of one block received, the clients do the decoding
operation to the packets and authenticate the messages.
At last, a new encoding rate
m
/
n
is determined by the server according to the es-
timated packet error rate
Q
(
m
/
n
= 1 -
Q
). With the block size parameter
n
adjusted
by the timeout threshold value, a pair of new values of
n
and
m
will be used.
4
Experiments and Results
We do our experiments under the local area network environment, and control the
network as three kinds of packet error model: random, stable and burst. One end
broadcasts the messages as the server, one end simulates the adversary to attack the
channel randomly, and other ends receive as the clients.
In our experiments, the server firstly sets
n
= 128,
m
/
n
= 1/2, and the transition
matrix scale as
k
= 8 (
O
i
= 0, 1/8,…, 7/8). Then it broadcasts a message, and the ad-
versary randomly attacks. The clients will receive the attacked packets and authenti-
cate them. During this period, the chosen nodes will send the feedback to the server
(here we ignore the error threshold and send every packet error rate back). The server
needs to gather the feedback values and then do the Markov estimation every 10 mi-
nutes. Also the time delay values are calculated and sent back in the same way.