Chemistry Reference
In-Depth Information
Chapter 5
Electrospinning of Chitosan (CHT)
Z. Moridi Mahdieh, V. Mottaghitalab, N. Piri, and A.K. Haghi
INTRODUCTION
Over the recent decades, scientists interested to creation of polymer nanofibers due to
their potential in many engineering and medical applications [1]. According to various
outstanding properties such as very small fiber diameters, large surface area per mass
ratio, high porosity along with small pore sizes and flexibility, electrospun nanofiber
mats have found numerous applications in diverse areas. For example in biomedical
field nanofibers plays a substantial role in tissue engineering [2], drug delivery [3], and
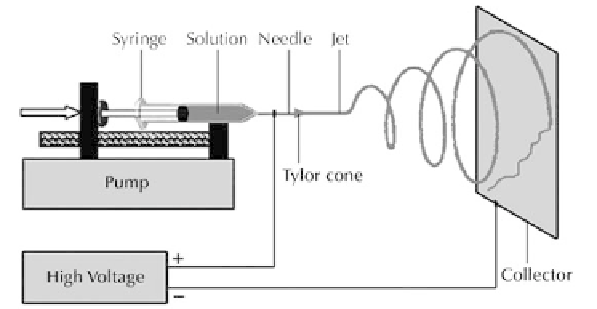
wound dressing [4]. Electrospinning is a sophisticated and efficient method by which
fibers produces with diameters in nanometer scale entitled as nanofibers. In electrospin-
ning process, a strong electric field is applied on a droplet of polymer solution (or melt)
held by its surface tension at the tip of a syringe needle (or a capillary tube). As a result,
the pendent drop will become highly electrified and the induced charges distributes
over its surface. Increasing the intensity of electric field, the surface of the liquid drop
will be distorted to a conical shape known as the Taylor cone [5]. Once the electric field
strength exceeds a threshold value, the repulsive electric force dominates the surface
tension of the liquid and a stable jet emerges from the cone tip. The charged jet then ac-
celerates toward the target and rapidly thins and dries because of elongation and solvent
evaporation. As the jet diameter decreases, the surface charge density increases and the
resulting high repulsive forces split the jet to smaller jets. This phenomenon may take
place several times leading to many small jets. Ultimately, solidification is carried out
and fibers deposits on the surface of the collector as a randomly oriented nonwoven mat
[6-7]. Figure 5.1 shows a schematic illustration of electrospinning setup.
Figure 5.1.
A typical image of electrospinning process [8].
















Search WWH ::

Custom Search