Chemistry Reference
In-Depth Information
macroscopic structure in the form of films, hydrogels, and fibers [157]. The CNT/
CS dispersions in acetic acid were spun into an ethanol: NaOH coagulation solution
bath. They were demonstrated increasing mechanical properties of wet spun fibers by
improving dispersion [158].
Electrospinning
In our recent work, the CS/MWNTs composite nanofiber were fabricated using elec-
trospinning. In our experimental researches, different solvents including acetic acid
1-90%, formic acid, and TFA/DCM were tested for the electrospinning of CS/CNT.
No jet was seen upon applying the high voltage even above 25 kV by using of acetic
acid 1-30% and formic acid as the solvent for CS/CNT. When the acetic acid 30-90%,
used as the solvent, beads were deposited on the collector. Therefore, under these con-
ditions, nanofibers were not formed.
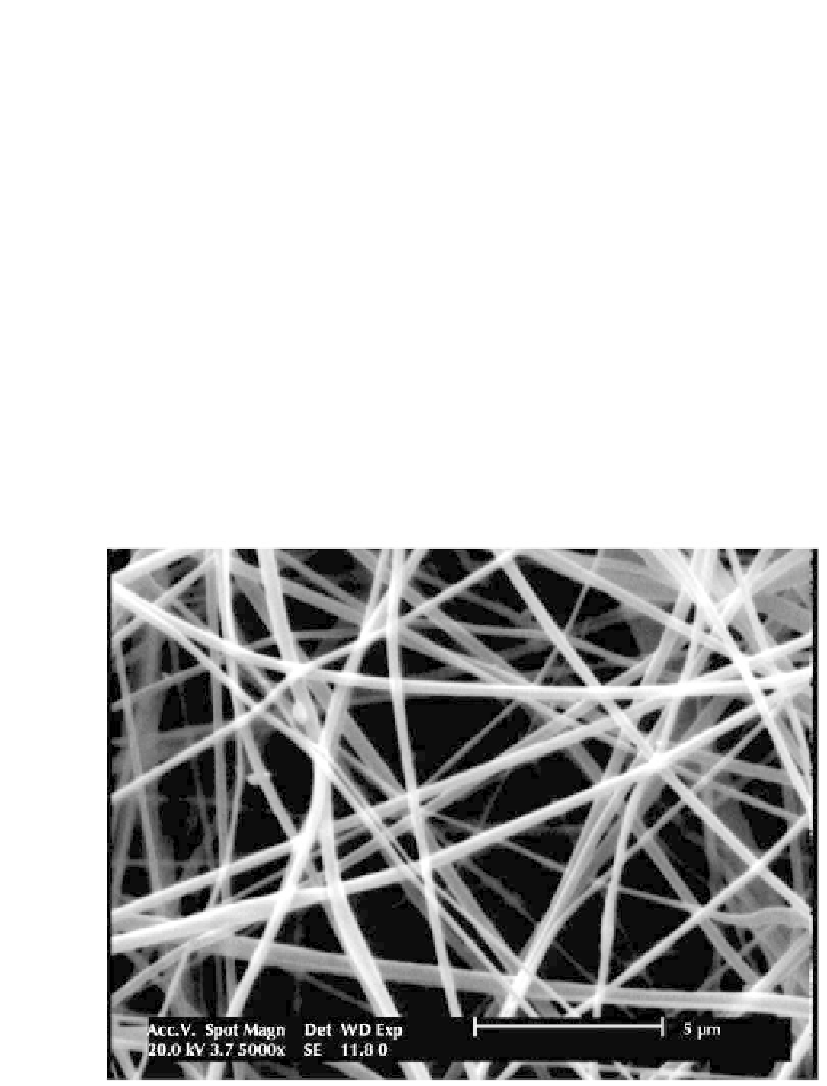
The TFA/DCM (70:30) solvent was only solvent that resulted for electrospinnabil-
ity of CS/CNT. The scanning electron microscopic (Fig. 7.7 showed the homogenous
fi bers with an average diameter of 455 nm (306-672) were prepared with CS/CNT
dispersion in TFA/DCM 70:30. These nanofi bers have a potential for biomedical
applications.
Figure 7.7.
SEM micrograghs of electrospun fibers of CS/MWNT at chitosan concentration of 10
wt%, 24 kV, 5 cm, TFA/DCM: 70/30 (0.06% wt MWNT).















Search WWH ::

Custom Search