Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
α
α
α
a
b
c
Closed
Open
Inactivated
Inactivation
loop
= Na
+
ions
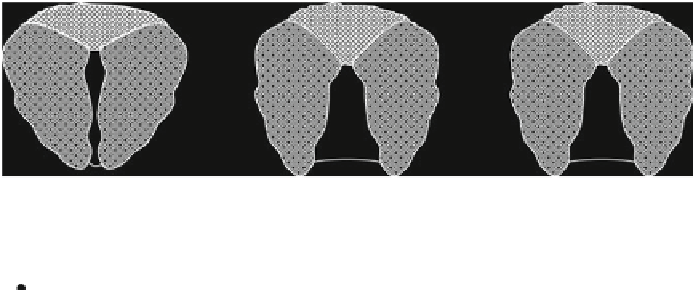
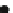
Fig. 2 VGSC functional states: (a) VGSC
a
-subunit in the resting state; (b) VGSC
a
-subunit in
the active state, when an inward Na
+
-subunit during fast
inactivation, when the intracellular loop connecting domains III and IV closes the inner entrance
of the conducting pore. Reprinted with permission from [
4
]. Copyright 2010 Elsevier
current is generated; (c) VGSC
a
then the channel turns into a nonconductive inactivated state by a mechanism
denominated fast inactivation. Immunohistochemical studies revealed a highly
conserved intracellular loop connecting domains III and IV of the
-subunit
(Fig.
1
). Mutagenesis experiments suggest that a hydrophobic triad of amino
acids (isoleucine, phenylalanine, and methionine) present in the loop, which is
called IFM motif, play a crucial role in fast inactivation by closing the intracellular
entrance of the conductive pore (Fig.
2c
). Moreover, the
C
terminus of the
a
-subunit
is likely to take part in the stabilization of the inactivated state. A number of
evidences support the existence of functional coupling between activation and
fast inactivation and indicate that the outward movement of the transmembrane
segment S4 in domain IV is most likely the signal to initiate fast inactivation. A
functionally and structurally different type of inactivation is slow inactivation. This
kinetic process occurs during either prolonged depolarizing plateaus or high fre-
quency repetitive firing and does not depend on the intracellular loop containing the
IFM motif, but involves a significant conformational change of the channel. During
slow inactivation, the channel continues to display residual conductance even at
very positive membrane potentials [
17
].
a
2.3 VGSC
a
-Subunit Subtypes and Their Localization
Nine functional
-subunits, indicated as Na
v
1.1-Na
v
1.9, have been cloned and
functionally expressed.
SCN1A
-
SCN5A
genes encode proteins Na
v
1.1-Na
v
1.5,
a