Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
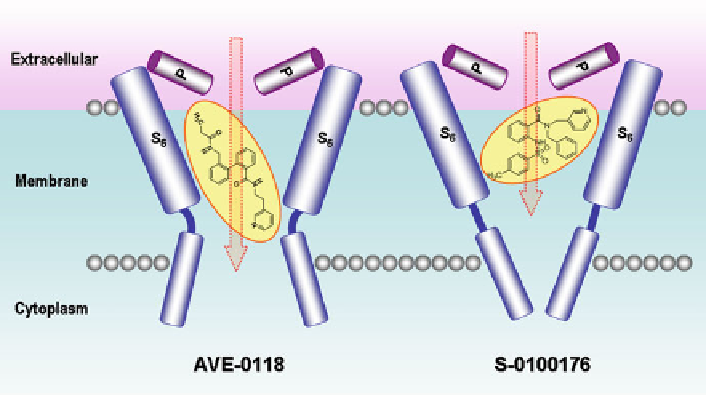
Fig. 5 The schematic binding mode of AVE0118 (24) and S-0100176 (37) with
K
v
1.5
channel
The prior computational work on
K
v
1.5
channel and ligands was carried out by
Luzhkov et al. The homology model of
K
v
1.5
channel protein was built based on
the crystal structure of KcsA potassium channel, which shared 54% sequence
identity with
K
v
1.5
channel, even if KcsA lacks the highly conserved Pro-X-Pro
motif in the S6 domain. S-0100176 (37) was used to validate the homology model.
The docking results showed that the aromatic framework of 37 was located in
a strong hydrophobic environment, where the pyridyl group faced downward to
Ile508, the benzamide phenyl ring faced upward to Thr479 and Thr480, and the
sulfonylamino moiety was close to Val505 while the toluene group was adjacent
to Val512 [
113
].
Then Pirard and co-workers established a structure-based virtual screening
protocol by using homology model of
K
v
1.5
potassium channel [
114
]. In addition,
by using Catalyst program, a three-hydrophobic-point pharmacophore was estab-
lished for the ligand-based virtual screening [
71
,
81
]. The comparison was made
and they concluded that structure-based strategy can be treated as complementary
with the ligand-based virtual screening method because of a higher hit rate.
More recently, our research group developed
K
v
1.5
homology model based on the
crystal structure of
K
v
1.2
potassium channel [
10
] since they shared 70% homology
identity and highly conserved S5/H5/S6 domains. The validation of this homology
model was carried out by the comparison of mutation data of S0100176 (37)and
AVE0118 (24)reportedbyDecheretal.[
111
,
112
] and KN-93 (38)reportedby
Fedida [
84
] through molecular docking. Further researches including the in silico
prediction of
K
v
1.5
inhibitory effects and the design of selective agents for the
treatment of atrial disorders are still ongoing [
115
].