Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
repolarization and refractoriness [
26
,
28
], which represents a promising approach to
treat atrial disorders [
29
-
31
].
In 1993, Nattel reported the in vitro prolongation of APD in atrial myocytes by
50
M of 4-Aminopyridine (4-AP) [
26
], which was then verified by follow-up
electrophysiological and computational experiments [
32
-
35
]. During recent years,
several pharmaceutical companies, including Icagen, Aventis, Merck, Eli Lilly,
Procter & Gamble (P&G), and Bristol-Meyers Squibb (BMS), have focused on
developing new structural types of
K
v
1.5
blockers [
36
,
37
]. Many different types
of
K
v
1.5
blockers have been designed and synthesized, and some of them are in
clinical trials.
m
3.3.1
ICA-32 and Analogues
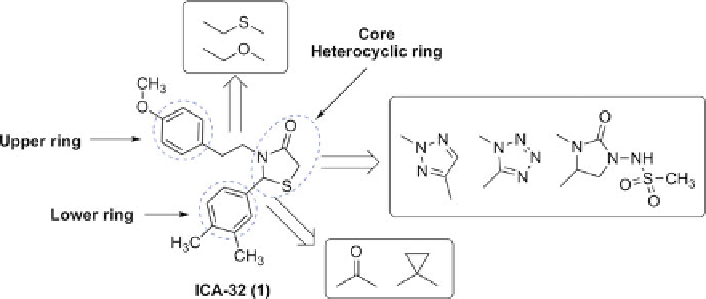
ICA-32 (1,IC
50
¼
M) was designed and synthesized by Icagen without any
pharmacological data published so far [
38
]. The framework of 1 contains a core
heterocyclic ring as well as the upper and lower ring, which were connected by
two flexible chain. Based on the structural analysis of 1, researchers in P&G
laboratories reported several series of analogues (Fig.
2
), including thiazolidine-
based derivatives [
39
], triazol derivatives [
40
], tetrazole derivatives [
41
], and
2-amino-2-imidazolidinone derivatives [
42
].
0.14
m
Thiazolidinone-Based Derivatives
In order to determine the contribution of vicinally substituted heterocycles
in ICA-32 framework, Jackson et al. started from the thiazolidinone scaffold
with two key structural modifications: (1) ketone instead of aldehyde-derived
thiazolidinones and (2) incorporation of the carbonyl group rather than the
Fig. 2 Modification strategy towards ICA-32 (1)