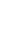
Database Reference
In-Depth Information
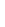
IBM
InfoSphere
Streams
Third-Party
In-Database
Analytics
Netezza
In-Database
Analytics
Software
Development
Kit
IBM SPSS
SAS
Tanay GPU
Appliance
by Fuzzy
Logix
Transformations
IBM SPSS
User-Defined
Extensions
(UDF, UDA,
UDTF, UDAP)
Revolution
Analytics
Mathematical
Geospatial
SAS 9.3+
IBM
InfoSphere
BigInsights
Predictive
Eclipse
Language
Support
(MapReduce,
Java, Python,
R, Lua, Perl,
C, C++,
Fortran,
PMML)
DBLytix by
Fuzzy Logix
Statistics
Time Series
Universal
PMML Plug-
In by Zementis
BI Tools
Cloudera
Data Mining
Visualization
Tools
Apache Hadoop
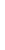
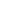
IBM Netezza AMPP Platform
Figure 4-5
The IBM Netezza analytics platform
Transformations
Execute in-database data transformations to realize signiicant
performance gains.
Mathematical
Perform deep in-database mathematical calculations to leverage MPP
processing.
Statistics
Calculate rich statistics without moving the data.
Timeseries
Create forecasts and identify trends using rich histories to improve
model accuracy.
Datamining
Use more data, or all of the data, to discover new and emerging insights.
Predictive
Move from batch processing to near-real-time speed-of-thought analytics
to predict with great accuracy and speed.
Geospatial
Implement location-based analytics on Big Data with immediate
feedback.
Table 4-1
In-Database Analytics Built into IBM Netezza Analytics
Extending the Netezza Analytics
Platform with Hadoop
As previously mentioned, the principle of massive parallelism and close-to-
source data processing (embodied by all parts of the IBM Big Data platform,
including Netezza, InfoSphere BigInsights [Hadoop], InfoSphere Streams,
and InfoSphere Data Explorer) provides enormous benefits for advanced
analytics running on large data sets. Because Hadoop and Netezza both
work on stored data, we want to explain when to use each, and how the two
technologies work together. Hadoop's ability to run on commodity servers,