Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
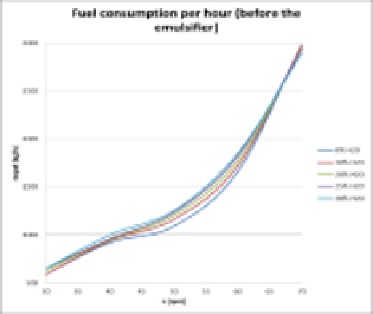
amount in the FWE have been recorded [12]. On the basis of the collected data, speed
characteristics were prepared demonstrating water and fuel consumption by the
engine supply system (Fig. 4).
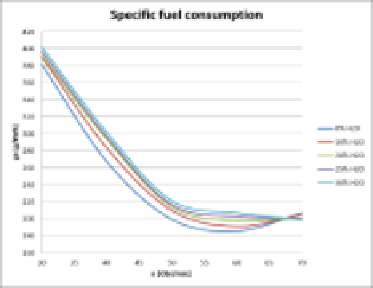
The analysis of data obtained during the exercise shows that the specific fuel
consumption increases as a result of injecting water into the cylinders, so the engine
total efficiency decreases for all the cycles in terms of speed up to 60 rpm. For water
amount of 25% and 30% m/m a change of the minimal fuel consumption was
observed at the speed from 60 to 70 rpm and a minimal fuel consumption decrease
close to the speed of 70 rpm (in comparison with results obtained for lower amount of
water in the FWE). It can be justified by a change of combustion conditions (high
engine loads and big amounts of water in the FWE) making the mixture more
homogenously flammable. The research presented in [10] confirmed the possibility of
a local decrease of the specific fuel consumption for given ranges of the engine load
and water amount in the FWE. It is also affected by the operation of mechanical and
pneumatic system of variable injection timing of fuel (VIT), which was implemented
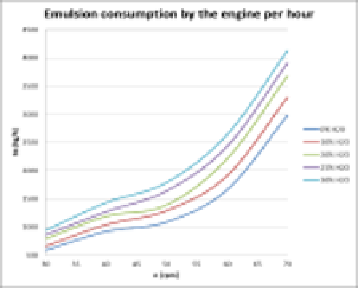
for the described simulator [17]. In the whole range of engine loads together with an
increase of water amount in the FWE there is an increase of the engine emulsion
consumption per hour for all measurements. This results from a higher energy
demand.
Fig. 4.
Speed characteristics of the main engine supply system)

Search WWH ::

Custom Search