Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
TABLE 8.1
International Classification of Enzymes: Code Numbers (EC 1st Digit, 2nd Digit, 3rd Digit,
4th Digit) and Types of Reactions CatalyzeddCont'd
1st Digit (Class)
2nd Digit
3rd Digit
4th
4. Lyases
Nonhydrolytic removal of groups
with product usually contains
double bond
Type of bond broken
1C
e
C
2C
e
O
3C
e
N
4C
e
S
5 C-halide
6P
e
O
99 Other
Group removed
1 Carboxyl
2 Aldehyde
3 Ketoacid
5. Isomerases
Type of reaction
1 Racemizationor epimerization
2 cis
e
trans isomerizations
3 Intramolecular oxidoreductases
4 Intramolecular transfer reactions
5 Intramolecular lyases
99 Other
Type of molecule
1 Amino acids
2 Hydroxyacids
3 Carbohydrates
6. Ligases
Synthesis of bonds with breaking
down of ATP or nucleoside
triphosphates
Type of bond formed
1C
e
O
2C
e
S
3C
e
N
4C
e
C
5 Phosphoric ester
6 N-metal
(a)
(b)
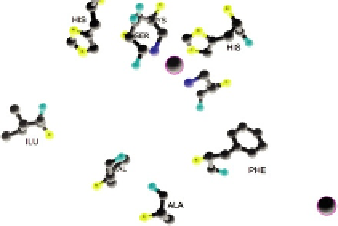
FIGURE 8.1
Alcoholdehydrogenase: structure and active sites. (a) Crystallographic structure of human ADH 5.
(b) The active site consists of a zinc atom, His-67, Cys-174, Cys-46, Ser-48, His-51, Ile-269, Val-292, Ala-317, and Phe-319.
The zinc coordinates the substrate (alcohol). The zinc is coordinated by Cys-146, Cys-174, and His-67, Phe-319, Ala-317,
His-51, Ile-269, and Val-292 stabilize NAD
þ
by forming hydrogen bonds. His-51 and Ile-269 form hydrogen bonds with
the alcohols on nicotinamide ribose. Phe-319, Ala-317, and Val-292 form hydrogen bonds with the amide on NAD
þ
.







Search WWH ::

Custom Search