Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
1. A projection of the point
P
on the sensor plane in the circle relative to cone 1.
2. A projection of the point
P
on the sensor plane in the circle relative to cone 2.
3. Two projections of the point
P
on the sensor plane, that is, each twin laser beam makes
a projection of the particle on the CCD array detector.
The last situation is interesting because we demonstrate that it is possible to find the path of
a point
P
A
(
C
1
,
2
) using the information on the projections' coordinates, by the
knowledge of the position of the two vertices
C
1
,
C
2
. Suppose that the projections' of
P
in
the two circles are the points
P
1
(
x
p
1
,
y
p
1
,0) and
P
2
(
x
p
2
,
y
p
2
,0), respectively, the point
P
can be
estimated as
Ω
1
)
-
(
C
2
,
Ω
P
5
C
1
P
1
-C
2
P
2
(10.5)
where
AB
denote the segment joining the points
A
(
x
A
,
y
A
,
z
A
) and
B
(
x
B
,
y
B
,
z
B
):
8
<
x
0
5
x
A
1
l
x
t
y
0
5
y
A
1
l
y
t
z
0
5
z
A
1
l
z
t
(10.6)
:
where
ðx
0
; y
0
; z
0
Þ
A
AB;
t
A
[0,1] and
l
ð
U
Þ
5
ð
U
Þ
B
2
ð
U
Þ
A
.
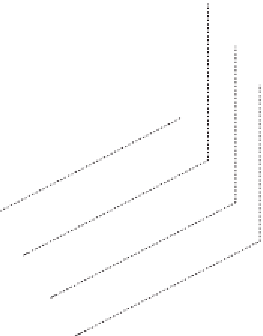
(A)
Estimated path
Real path
(B)
200
200
100
100
0
0
-100
-100
-200
-200
-200
-200
-100
-100
-2.5
0
0
-2
-2
-1.5
0
×
10
4
×
10
4
100
100
-1
-0.5
2
x
(pixels)
x
(pixels)
200
z
(pixels)
200
z
(pixels)
0
Figure 10.9
Comparison between real and estimated path for (A) linear and (B) coil paths.




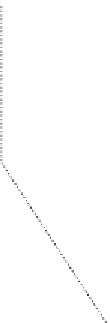
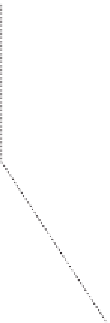



















































































































Search WWH ::

Custom Search