Hardware Reference
In-Depth Information
no apologies are made for repeating it. In the heat of the moment it is all too
easy to forget that a system is 'live'. You are only likely to make this mistake
once - but the cost and frustration are likely to have a long-lasting effect!
Address decoding
The I/O provided by an expansion card will be mapped into either address or
I/O space (the latter being conventionally used for digital and analogue I/O
cards). The expansion card must, therefore, contain some address decoding
logic which must be configured to avoid conflicts with other system hardware.
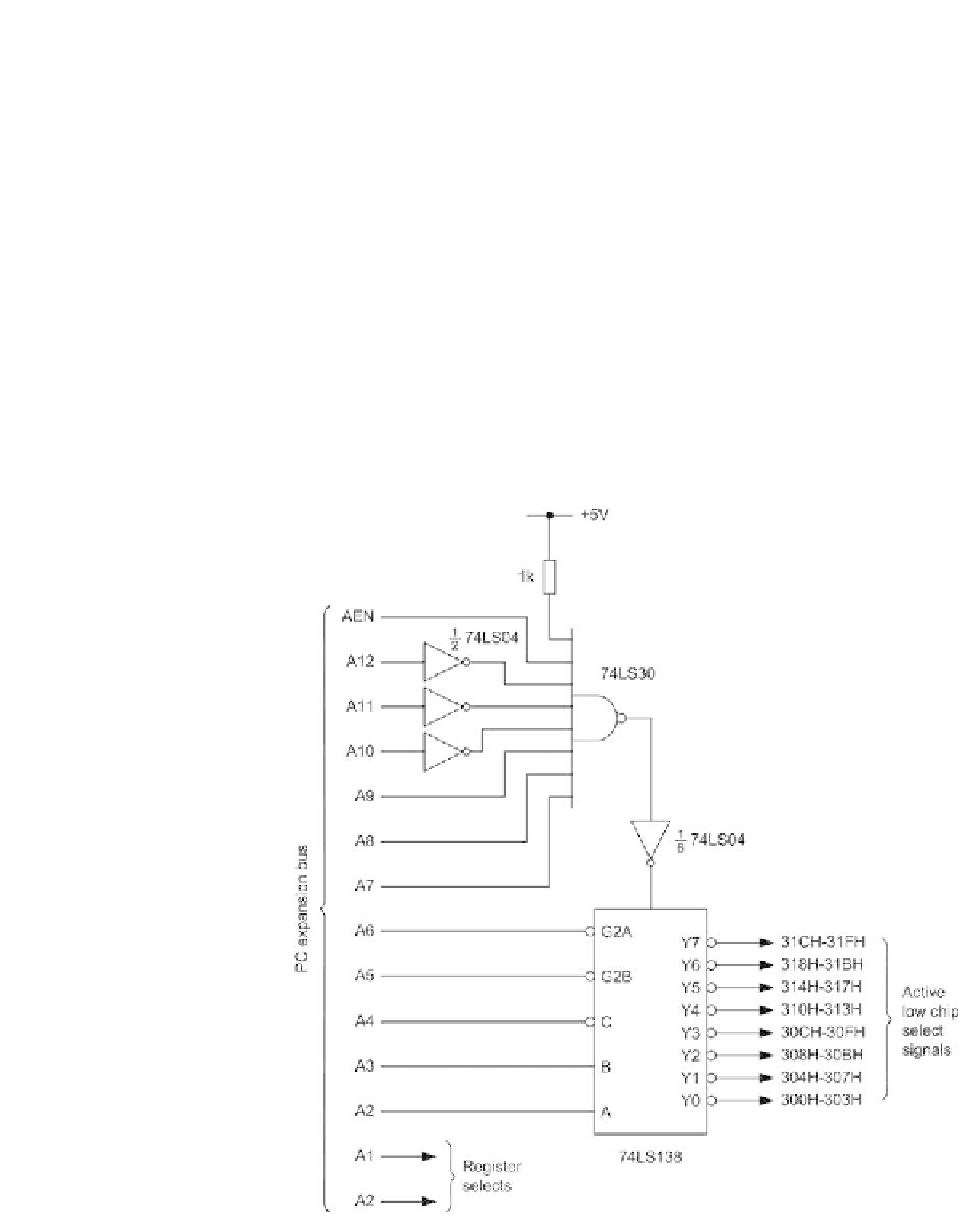
Figure 2.5 shows some representative address decoding logic which provides
access to eight
base addresses
within I/O space. Address lines A0 and A1 may
then be used as optional
register select
lines for connection to VLSI devices
(e.g. an 8255 Programmable Parallel Interface).
The address decoder shown in Figure 2.5 employs a three-to-eight line
decoder (74LS138) in which the enable lines (G2A, G2B, and G1) are employed
(note that G2A and G2B are active low, whilst G1 is an active-high input).
Figure 2.5
Representative address decoder arrangement