Image Processing Reference
In-Depth Information
8
:+8$(00)
!!)($
)
!!)0
+
8
$(
0
);
*@
4-
-
C
*04
# !+8$(00)<+8
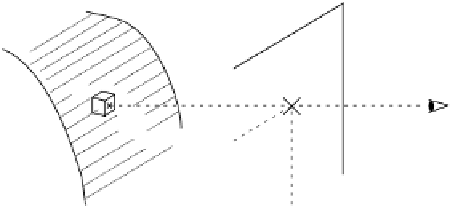
Fig. 7.17.
Illustration of gradient shading [Hoehne86].
of a point P
perpendicular to the image plane
L
. Then a density
g
i
j
k
=
(
i
,j
) on the image plane
L
is given as follows.
g
i
j
k
=
A
cos
{
(
f
i,j
+1
,k
−
f
ijk
)
/B
}
,
(7.17)
where
f
i
j
k
= a density value of a 3D gray-tone image before binalization,
A, B
= suitable constants.
This method is called
gradient shading
[Hoehne86]. This enables us to
render a 3D gray-tone image by treating it as if light reflected by some surface
has a virtually normal vector. This method is frequently used in combination
with the volume rendering for visualization of medical CT images.
Remark 7.14.
In the virtualization methods discussed here, a viewpoint and
view direction are selected arbitrarily. Therefore, we can select a physically
unrealizable viewpoint inside the human body. Furthermore, by generating a
sequence of images while viewing an object from continuously moving view-
points, we can present a moving image looking as if it is flying through the
inside of a 3D solid object. This technique has recently gained popularity
when observing 3D CT images in medicine. This is called
virtual endoscopy
,
because it is regarded as a simulation of an endoscope. Sometimes it is called
by the name of a target organ to which it is applied, like virtual colonoscopy
and virtual bronchoscopy [Rogalla01].




Search WWH ::

Custom Search