Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
Table 3.
The experiment results of ICMP covert channel detection
Test Set1 Test Set2
Training Set Kernel Features FP FN TC FP FN TC
13 2.5 0.4 97.1 0.7 0.7 98.6
Training Linear 15 1.1 0.8 98.1 0 0.6 99.4
Set1 13 0.2 0.6 99.2 0 0.8 99.2
Polynomial 15 0.8 0.6 98.6 0 0.8 99.2
13 24.3 0.8 74.9 12.1 1.6 86.3
Training Linear 15 0 0.8 99.2 0 0.6 99.4
Set2 13 3.8 0.6 95.6 2.5 1.0 96.5
Polynomial 15 0.8 0.6 98.6 0 0.2 99.8
*The degree of Polynomial Kernel = 3, FP = False Positive(%),
FN = False Negative(%), TC = Total Correctness(%)
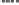
Correctness
False Positive
False Negative
100
90
80
70
60
50
40
30
20
10
1.65
0.7
0.7
0.7
0.55
0.5
0.1
0.4
Polynomial Kernel,
15 Features
Linear Kernel,
13 Features
Linear Kernel,
15 Features
Polynomial Kernel,
13 Features
The Result of Training Set1
Fig. 2.
The results of Training Set1
rest 4 bytes of ICMP header. We classified training set into training set 1 with
generally used ICMP packets and training set 2 with ICMP packets depending
on operating system. The experiment environment has been performed in a lab-
oratory test bed. The experiment results show that the detection provided by
SVM method is very ecient for ICMP covert channel.
References
1. John McHugh: Covert Channel Analysis. Portland State University (1995)
2. Loki: ICMP Tunneling, daemon9, Pharack Magazine, Volume 6, Issue 49
3. Vapnik V.,
“The Nature of Statistical Learning Theory”
, Springer-Verlag, NY (1995)
4. Bellovin, S.M.: Security Problems in the TCP/IP protocol suite. Computer Com-
munication Reviews, 19(2) (April 1989) 32-48
5. Mukkamala, S., Janowski, G.: Intrusion Detection Using Neural Networks and Sup-
port Vector Machines. Proceedings of IEEE IJCNN (May 2002) 1702-1707
6. Joachmims T,“mySVM - a Support Vector Machine”, Univerity Dortmund