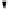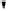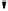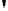Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
AES candidates MARS [7] and RC6 [8] in which all bits of the controlling data sub-
block influences the selection of the current value of the rotation, the number of dif-
ferent modifications of the DDR is small though. A more efficient way to define
significant role of each bit of the controlling data subblock is the use of DDP having
very large number of different modifications. Design of ciphers based on DDP ap-
pears to be a new and perspective direction in applied cryptography [1-3] oriented to
the use of very cheap hardware.
Two new block ciphers, SPECTR-H64 and CIKS-1, based on DDP were devel-
oped the last two years [1-2]. In these ciphers, the appropriate data diffusion is
achieved due to the use of DDP having 2
48
and 2
80
bit permutation modifications. In
these ciphers the DDP are performed with the operational boxes P
n/m
(Fig.1), where
n
is the size of the input and
m
is the size of the controlling input. A P
2/1
box is con-
trolled by one bit
v
. It swaps two input bits, if
v
= 0, otherwise (
v
= 1) the bits are not
swapped. In general the value
v
is assumed to be dependent on encrypted data and/or
key bits. For a given P
n/m
box, suppose an arbitrary input bits
x
1
,
x
2
, …,
x
h
, with
n
≥
h
and arbitrary
h
output bits
y
1
,
y
2
, …,
y
h
there is at least one CP-modification moving
x
i
to
y
i
for all
i
= 1, 2, …,
h
. Such a P
n
/
m
box is called a CP box of order
h
.
Fig. 1.
CP boxes: P
n/m
(a), P
2/1
(b), P
4/4
(c), and P
-1
4/4
(d)
It is quite evident that the box P
-1
n
/
m
is of order
h
, if the box P
n
/
m
is of order
h
. The
maximal order of the CP box P
n
/
m
is equal to
n
. The set of CP-modifications of the P
n
/
m
box of maximum order contains all of
n
! possible bit permutations. The P
n/m
boxes of
the orders
h
= 1, 2, 4, …,
n
, where
n =
2
k
, are described in [3]. The CP boxes used in
both SPECTR-H64 and CIKS-1 consist of a number of layers. Each layer contains
n
/2 parallel P
2/1
boxes. The CP box consists of 2
m
/
n
P
2/1
-layers. The concatenation of
all controlling bits corresponding to the
l
th layer we call the
l
th controlling substring
V
(
l
). By swapping the input and the output of an arbitrary given P
n/m
box one can
easily construct a respective inverse P
-1
n/m
box, with the same controlling substring