Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
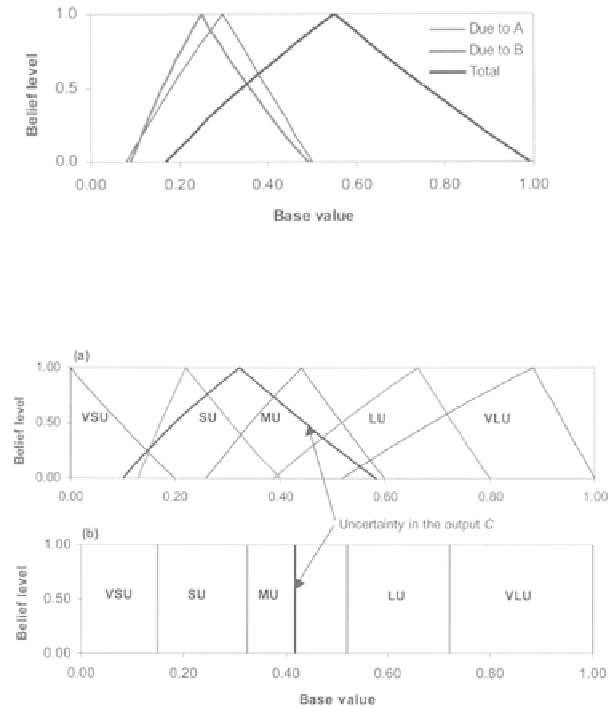
Figure 4.11.
Estimated uncertainty in the output
C
=
f (A, B)
.
Figure 4.12.
Example of presenting uncertainty in (a) fuzzy and (b) crisp
qualitative uncertainty scales. The estimated uncertainty in the output
C
is shown in a thick-dark line.
4.4
Towards hybrid techniques of modelling uncertainty
A hybrid technique of uncertainty modelling is defined here as a method that makes use
of both probabilistic and possibilistic approaches together. Although there are some
analogies, the concepts that lead to the formulation of probability theory and possibility
theory are very different. The former considers uncertainty as random, whereas the latter
assumes uncertainty due to imprecision and vagueness (Ross, 1995). In order to analyse
the situations where both types of uncertainty are present two types of problem are
distinguished: these are referred to as Type I Problem and Type II Problem.
Search WWH ::

Custom Search