Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
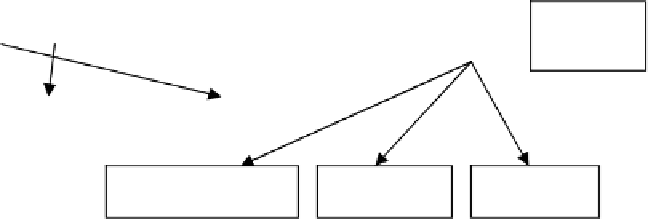
Scriptset level (defining a set of general attack intentions)
Script level (determining a general attack intention)
Script stages
Backdoors
creation
Reconnais-
sance
Implantation
Gaining
privileges
Threat
realization
…
…
OS
determination
Port scanning
Confidentiality
violation
Availability
violation (DoS)
Integrity
violation
1. Delete files
2. Delete by Virus
…
1. Read File
2. Read by Virus
…
1. SYN flood
2. Land
…
Fig. 3.
Fragment of generalized attack model
5 Model of Analyzed Computer Network
The model of analyzed computer network (system) intends for evaluating attack re-
sults and defining system reaction. It contains the following basic components (fig.4):
network interface; module of malefactor actions recognition; module of attack result
evaluation; module of system response generation; database about analyzed system,
database of attack signatures.
Network interface
provides: (1) receiving identifiers and parameters of attacks; (2)
transferring attack results and system reactions.
Module of malefactor actions recognition
is necessary at realization of detailed at-
tack modeling and simulation, i.e. when malefactor actions are represented as network
packets. Functioning of this module is based on a signature method - the data re-
ceived from the network interface are compared to signatures of attacks from
data-
base of attack signatures
. Outputs of the module are identifiers and parameters of
attacks.
The knowledge base about analyzed system
is created from the specification of
analyzed system and structurally coincides with KB about analyzed system described
in section 3. The difference of these knowledge bases consist in the stored data: KB of
the model of analyzed system contains the results of translating the specifications of
analyzed system; KB related to the generalized architecture of SAS is initially empty
and is filled during the execution of attack scripts.
Formal representation of analyzed system includes the specification of computer
network structure, hosts resources and functions. The structure of a computer network
CN
is determined as follows [9]:
M
CN
= <
A, P, N, C
>, where
A
is the network ad-
dress;
P
is a family of protocols used (e.g., TCP/IP, FDDI, ATM, IPX, etc.);
N
is a set