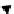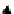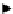Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
where lignocellulose is utilised as a feedstock for platform molecule production,
the lignin is left as a waste and often burnt for energy recovery. There are examples
where the use of ionic liquids for the processing lignocellulose has produced
aromatic compounds (e.g. guaiacol, eugenol and vanillin) from lignin, where it is
found that different biomasses lead to different aromatic products [70]. However,
commercialisation of an ionic liquid process could prove difficult due to the cost,
toxicity and difficult product recovery when using this class of solvent. Alternatively,
technologies for the specific depolymerisation of lignin can be applied to lignin
residues, some examples of which are described in the following section.
Various other polysaccharides are also available from waste biomass in appre-
ciable quantities and can also be applied to the production of platform molecules.
Inulin for example is a fructan found in various plants that is historically isolated
from chicory, though Jerusalem artichoke tubers also contain inulin in excess of
70% dry weight and are commercially cultivated [71]. Although inulin can be
hydrolysed to fructose prior to conversion to platform molecules [72], it is also
often found that the polysaccharide itself can be converted directly into these
same molecules (HMF, CMF, etc.) [19, 73]. A greater issue in its use as feedstock
for platform chemicals is its overall abundance, which is much lower than for the
lignocellulose components (lignin, cellulose and hemicellulose). There are some
natural polysaccharides that contain heteroatoms other than oxygen and, as such,
these could present alternative possibilities in the future of platform molecule
production (Figures 4.6 and 4.7). Chitin for instance is a nitrogen-containing
polysaccharide that is abundant and widely available as a by-product of the
seafood industry, forming the major constituent of the exoskeletons of crusta-
ceans. Chitin, which can be de-acetylated to chitosan, is predominately used in
commercial products in its polymeric form (e.g. thickener in foods and binder in
textiles) but can be hydrolysed to its glucosamine monomer and, with further
processing, this could also be utilised a platform molecule (Figure 4.6) [74]. It has
recently been demonstrated that chitin can be converted directly into
OH
NH
2
O
HO
O
O
HO
O
NH
2
OH
Chitosan
OH
O
OH
NH
Seafood
waste
O
HO
O
Hydrolysis
O
O
HO
HO
O
HO
NH
NH
2
Glucosamine
O
O
OH
OH
O
Chitin
O
3-acetamido-5-
acetyl furan
N
H
Figure 4.6
Potential for platform molecules derived from chitin.