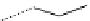Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
O
O
5-methylfurfural
OSO
-
O
O
Extraction
Pyrolysis
O
O
Seaweed
O
O
-
O
3
SO
OH
OSO
-
Furfural
Fucoidan
S
O
2-methoxy-5-methyl-
thiophene
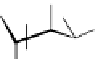
Figure 4.7
Potential for platform molecules from seaweed-derived sulphur-containing
polysaccharides.
3-acetamido-5-acetyl furan, a nitrogen-containing furan, and although yields
were low this still represents an interesting application of this widely available
polysaccharide [75]. Sulphur-containing polysaccharides can also be found
naturally, examples including fucoidan and carrageenan, which are naturally
present in seaweeds. Pyrolysis of these polysaccharides has led to the formation
of typical platform molecules produced from cellulose and hemicellulose, such as
furfural and 5-methylfurfural, but also to some uncommon heteroatom derivatives
such as 2-methoxy-5-methyl-thiophene (Figure 4.7) [76, 77].
4.4.2
Lignin
Lignin represents a significant proportion of lignocellulosic material and is
considered the largest potential source of bio-based aromatics. However, the
complex character and physical and chemical robustness of the lignin structure
has resulted in little success in the effective valorisation of lignin beyond burning
(energy recovery), gasification and use in niche applications as a dispersant,
binder, adhesive and as a precursor to carbon fibre [78-80].
Lignin is highly recalcitrant relative to the other major constituents of lignocel-
lulose, and has proven resistant to most biological and chemical degradation
treatments [81]. Some technologies are however available, or under development,
for the conversion of polymeric lignin into smaller molecules that are useful as
building blocks for the biorefinery. Research efforts to date focus on the produc-
tion of platform chemicals from lignin (Figure 4.8) either by pyrolysis or chemical
depolymerisation (including hydrothermal hydrolysis and hydrogenolysis).
Pyrolysis is performed rapidly at high temperatures (>500°C) and pressures,
producing a mixture of gases, char and bio-oil (a highly complex mixture of
organic compounds) [82]. It is unlikely that pyrolysis will be used to produce
specific platform molecules from lignin due to the complexity of the bio-oil