Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
Phe538
Q Switch
M Site
Zn
Mg
Gln535
Ile502
P Clamp
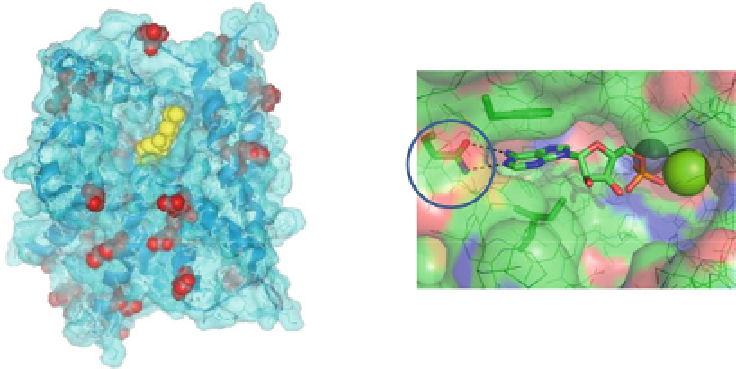
Fig. 4 Architecture of the PDE4 catalytic domain and active site. (
Left
) Surface-rendered view of
the PDE4D catalytic domain (
blue
) with roflumilast (
yellow
) bound in the active site. Amino acids
that differ between PDE4D and PDE4B are colored
red
. There are no sequence differences within
the active site that can be used to achieve subtype selectivity. (
Right
) Surface-rendered view of the
PDE4 catalytic site. The invariant glutamine (Gln535), hydrophobic P-clamp (Ile502 and Phe538),
and the M-site comprising the catalytic metals are indicated
present in all PDEs. Surrounding residues anchor the glutamine in orientations that
allow hydrogen binding to a ring nitrogen of cAMP or cGMP. Competitive PDE4
inhibitors have also been optimized for interaction with binding pockets in the
PDE4 active site or for interaction with the catalytic metals (Wang et al.
2007a
).
The absolute sequence conservation of the PDE4 active site across the PDE4A-D
subfamilies has made it difficult to develop subtype selective PDE4 inhibitors
(Fig.
4
). Indeed, potent compounds such as roflumilast are equipotent against
PDE4A-D (Fig.
5
).
Cilomilast and roflumilast are the competitive PDE4 inhibitors for which the
most extensive clinical data are available. The compounds were developed for
treating respiratory disease with a particular focus on asthma and chronic obstruc-
tive pulmonary disorder. Both compounds show noninferiority to inhaled steroids
in mild-to-moderate asthma supporting the therapeutic concept of PDE4 inhibition
(Reid
2002
; Giembycz
2005
,
2006
; Lipworth
2005
; Spina
2008
). Key features
of asthma are the recruitment of inflammatory cells to lung and airway hypersen-
sitivity, both of which are blunted by PDE4 inhibitors. Eosinophils are sensitive to
inhibition of PDE4D (Chambers et al.
2006
), while inflammatory activation of
monocytes is sensitive to PDE4B inhibition (Jin and Conti
2002
; Spina
2008
).
Measurement of eosinophil or monocyte activation in human whole blood thus
provides a convenient pharmacodynamic marker of PDE4 inhibition and a metric
by which to evaluate therapeutic margin as shown in Table
3
. Comparing the two
compounds, roflumilast is the more potent PDE4 inhibitor with an in vitro IC
50
of 2 ng/ml for inhibition of eosinophil production of leukotriene E4 (LTE4).
Monocytes are tenfold less sensitive to roflumilast
than eosinophils with an