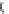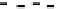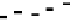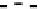Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
100
100
100
PDE4D7
PDE4D7
PDE4B1
PDE4B1
75
75
75
PDE4D7
PDE4B5
PDE4B5 C-trunc
PDE4B1
50
50
50
25
25
25
0
0
0
-6
-5
-4
-3
-2
-1
0
1
2
10
-6
10
-5
10
-4
10
-3
10
-2
10
-1
10
0
10
1
10
2
10
3
-6
-5
-4
-3
-2
-1
0
1
2
3
10
10
10
10
10
10
10
10
10
10
10
10
10
10
10
10
10
10
10
10
10
Roflumilast (µM)
33 [µM]
D159153 [µM]
PDE4B5
PDE4B5 C-trunc
PDE4 Enzyme Coupled Real Time Kinetic Assay
O
Cl
N
H
O
N
F
N
H
COOH
NH
2
N
N
Cl
O
F
N
F
O
O
S
Cl
NO
2
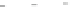
roflumilast
D159153
33
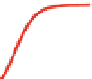
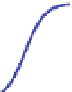
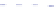
Fig. 5 Inhibition of PDE4 enzymatic activity by compounds exploiting ligand-binding modes
unique to the three PDE4 conformers. Roflumilast binds the open PDE4 conformer competitively
with cAMP, inhibits the enzyme completely (
I
max
100%), and has no subtype-selectivity for
PDE4D versus PDE4B. D159153 binds the asymmetric PDE4 conformer noncompetitively with
cAMP, there is a ceiling to the maximum inhibition of PDE4D (
I
max
¼
90%), and the compound
shows subtype selectivity due to the Phe/Tyr polymorphism in UCR2. Compound 33 (Naganuma
et al.
2009
) may bind the symmetric closed PDE4 conformer with the C-terminal helices capping
both active sites. Compound 33 inhibits PDE4 completely (
I
max
¼
100%) and has subtype-
selectivity for PDE4B over PDE4D. Potency and PDE4B selectivity require the C-terminus. It
inhibits long (PDE4B1) and supershort (PDE4B5) subtypes of PDE4B with equal potency.
Truncation of the PDE4B5 C-terminus causes a 150-fold drop in potency from an IC
50
¼
¼
0.09
m
M
against PDE4B5 to an IC
50
14
m
M when the C-terminus is removed. D159153 and compound
33 share a common chemotype characterized by a planar, aromatic ring from which a pair of
aromatic arms project. Biochemical assay data were generated using a novel, real-time kinetic
assay (Box) in which hydrolysis of cAMP is coupled to NADH formation, which can be measured
spectroscopically (Burgin et al.
2010
)
¼
in vitro IC
30
of 20 ng/ml with respect to inhibition of lipopolysaccharide-
stimulated production of tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF
a
) (Hatzelmann and
Schudt
2001
). The clinical dose of roflumilast explored in human clinical trials
(0.5 mg once daily) exceeded the no observable effect level (NOEL) for emesis
(Table
3
). Roflumilast was emetic in 8% of subjects at that dose. Emesis in
animals occurs quickly and violently after dosing with such a PDE4 inhibitor,
suggesting that emetic threshold is driven by the rising or maximum concentration
reached by the drug. The clinical dose of roflumilast achieved a
C
max
of 3.9 ng/ml
in plasma and a steady-state average concentration (
C
av
) of 1.5 ng/ml. Thus, the
clinical dose of roflumilast did not produce sustained blood levels greater than the
IC
50
for in vitro inhibition of eosinophil and monocyte inflammatory responses.
Presumably, additional therapeutic benefit would be obtained if the dose could be
increased, but dose escalation is limited by tolerability. Emesis can be reduced to
some extent by designing PDE4 inhibitors that distribute poorly to the brain (Aoki
et al.
2001
), but the trade-off may be high plasma protein binding, poor cellular
permeability, or low oral bioavailability.