Hardware Reference
In-Depth Information
day for users who experienced 200 ms delays, and there were 0.2% fewer searches from users
who experienced 400 ms delays. Given the amount of money made in search, even such small
changes are disconcerting. In fact, the results were so negative that they ended the experiment
prematurely [
Schurman and Brutlag 2009
].
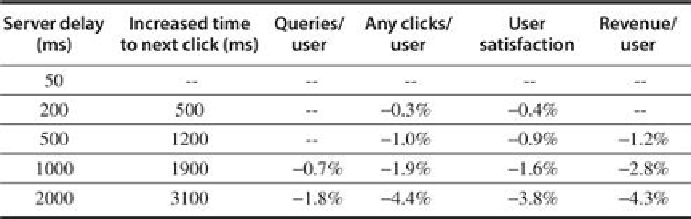
FIGURE 6.12
Negative impact of delays at Bing search server on user behavior
Because of this extreme concern with satisfaction of all users of an Internet service, per-
formance goals are typically specified that a high percentage of requests be below a latency
threshold rather just offer a target for the average latency. Such threshold goals are called
ser-
vice level objectives
(
SLOs
) or
service level agreements
(
SLAs
). An SLO might be that 99% of re-
quests must be below 100 milliseconds. Thus, the designers of Amazon's Dynamo key-value
storage system decided that, for services to offer good latency on top of Dynamo, their storage
system had to deliver on its latency goal 99.9% of the time [
DeCandia et al. 2007
]. For example,
one improvement of Dynamo helped the 99.9th percentile much more than the average case,
which reflects their priorities.
Cost Of A WSC
As mentioned in the introduction, unlike most architects, designers of WSCs worry about op-
erational costs as well as the cost to build the WSC. Accounting labels the former costs as
oper-
ational expenditures
(
OPEX
) and the later costs as
capital expenditures
(
CAPEX
).
To put the cost of energy into perspective,
Hamilton [2010]
did a case study to estimate the
costs of a WSC. He determined that the CAPEX of this 8 MW facility was $88M, and that the
roughly 46,000 servers and corresponding networking equipment added another $79M to the
CAPEX for the WSC.
Figure 6.13
shows the rest of the assumptions for the case study.
Search WWH ::

Custom Search