Hardware Reference
In-Depth Information
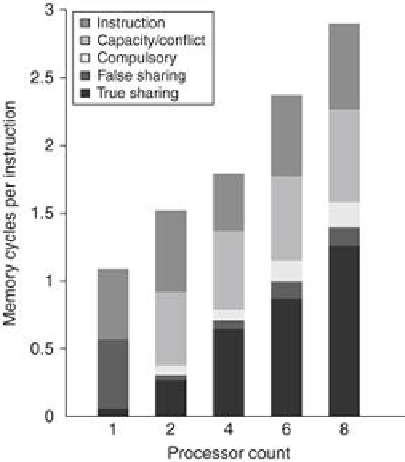
FIGURE 5.14
The contribution to memory access cycles increases as processor count
increases primarily due to increased true sharing
. The compulsory misses slightly in-
crease since each processor must now handle more compulsory misses.
The final question we examine is whether increasing the block size—which should decrease
the instruction and cold miss rate and, within limits, also reduce the capacity/conflict miss rate
and possibly the true sharing miss rate—is helpful for this workload.
Figure 5.15
shows the
number of misses per 1000 instructions as the block size is increased from 32 to 256 bytes. In-
creasing the block size from 32 to 256 bytes affects four of the miss rate components:
■ The true sharing miss rate decreases by more than a factor of 2, indicating some locality in
the true sharing paterns.
■ The compulsory miss rate significantly decreases, as we would expect.
■ The conflict/capacity misses show a small decrease (a factor of 1.26 compared to a factor of
8 increase in block size), indicating that the spatial locality is not high in the uniprocessor
misses that occur with L3 caches larger than 2 MB.
■ The false sharing miss rate, although small in absolute terms, nearly doubles.
Search WWH ::

Custom Search