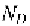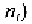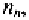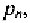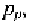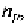Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
valence of three, gives us almost one free hole for every impurity atom. A
pentavalent atom donates electrons to the intrinsic silicon and is known as a
donor. In contrast, a trivalent atom accepts electrons and is known as an
acceptor. Typical pentavalent impurities, also called n-type dopants, are
arsenic, As, and phosphorus, P, while the most used trivalent impurity, also
called p-type dopant, is boron, B. Silicon doped with a pentavalent impurity
is said to be n-type silicon, while silicon doped with a trivalent impurity is
called p-type silicon.
If we suppose that a concentration of donor atoms (greater than the
intrinsic carrier concentration, is used to dope the silicon, the
concentration of free electrons in the n-type material,
can be assumed as
equal to
In fact, this is an approximation, since some of the free electrons of the
doping material recombine with the holes, but it is sufficient for as long as
condition is true.
The fact that some free electrons recombine with holes, also reduces the
concentration of holes in the n-type material,
to
Similarly, if we dope the silicon with a concentration
of acceptor
atoms, the concentration of free holes in the p-type material,
is equal to
while the electron-hole recombination reduces the concentration of free
electrons in the p-type material,
to
1.2 DIODES
A diode, or pn junction, is made by joining a p-type to an n-type material
as in Fig. 1.1. The p-side terminal is called anode (A) while the n-side
terminal is called cathode (K).