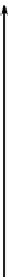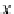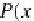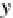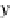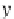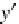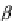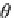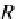Graphics Reference
In-Depth Information
Fig. 7.2
The point
P(x,y)
is
rotated through an angle
β
to
P
(x
,y
)
7.3.1 Translate a Point
Perhaps the simplest transform is that of point translation. For example, to translate
a point
P(x,y)
by
(t
x
,t
y
)
, we only require
x
=
x
+
t
x
y
=
+
t
y
which is represented by this homogeneous matrix
⎡
y
⎤
⎡
⎤
⎡
⎤
x
y
1
10
t
x
01
t
y
00 1
x
y
1
⎣
⎦
=
⎣
⎦
⎣
⎦
.
We will refer to this translate matrix as
T
t
x
,t
y
.
As an example, let's translate the point
P(
2
,
3
)
by
(
4
,
5
)
, which moves it to
P
(
6
,
8
)
:
⎡
⎤
⎡
⎤
⎡
⎤
6
8
1
104
015
001
2
3
1
⎣
⎦
=
⎣
⎦
⎣
⎦
.
7.3.2 Rotate a Point About the Origin
Figure
7.2
shows a point
P(x,y)
which is rotated an angle
β
about the origin to
P
(x
,y
)
, and as we are dealing with a pure rotation, both
P
and
P
are distance
R
from the origin.
From Fig.
7.2
it can be seen that
cos
θ
=
x/R
sin
θ
=
y/R
x
=
R
cos
(θ
+
β)
y
=
R
sin
(θ
+
β)