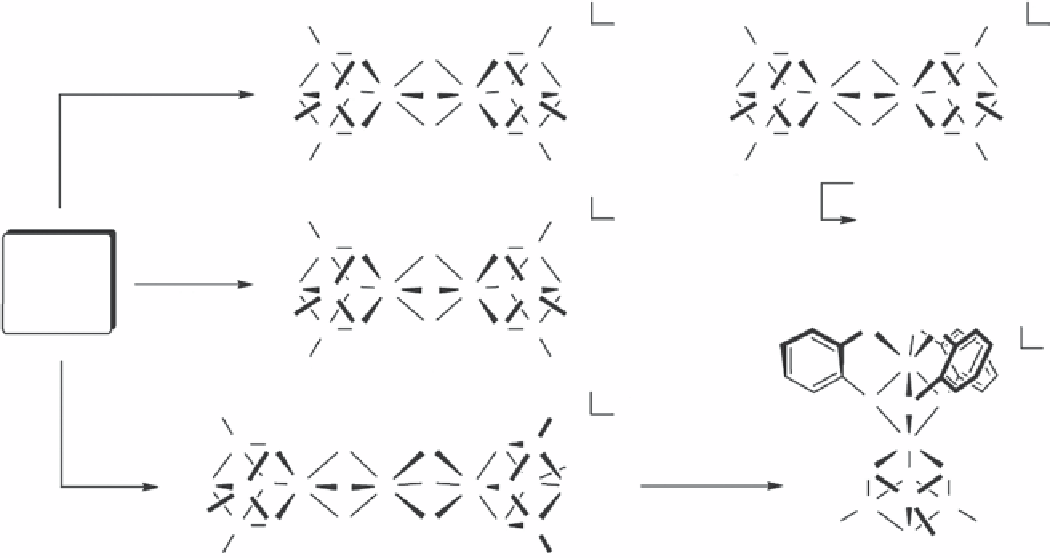Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
Mn(II) + Ca(II) + oxidant
3-
z
RS
SR
RS
SR
S
R
Fe
Fe
Fe
S
Fe
S
S
S
m
= 3,
n
~ 10
S
S
S
S
S
Mo
Mo
S
SR
+
S
Mo
Mo
S
SR
S
Fe
Fe
R
Fe
Fe
(2)
RS
RS
R
S
Fe
S
S
Fe
Fe
S
S
Fe
R
SR
RS
RS
SR
1
2
,
z
=3-
3-
RS
SR
2 Na(C
12
H
8
)
5
,
z
=5-
m
=3,
n
~ 2.5,
xs MeO
-
Me
Fe
S
S
Fe
[MoS
4
]
2-
/
m
FeCl
3
/
n
NaSR
Me
S
S
S
Mo
Mo
Fe
S
Fe
O
(4)
3
RS
SR
O
Fe
O
O
O
Fe
S
S
3-
Me
RS
SR
Fe
4
O
O
3-/4-
O
6
RS
SR
S
S
Mo
Fe
S
S
Fe
6
o
-C
6
H
4
(OH)
2,
12 Et
3
N
m
= 3.5,
n
~ 12
SR
R
S
S
S
S
Fe
Mo
Mo
S
Fe
R
Fe
S
S
Fe
(3)
Fe
Fe
RS
R
R
Fe
S
S
Fe
RS
SR
S
SR
RS
SR
3
6
sCheme 25.2
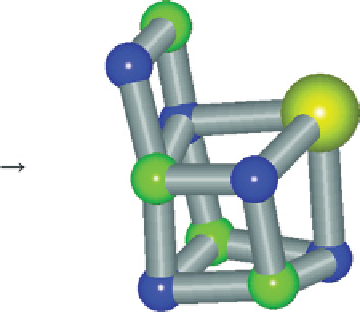
Self-assembly of inorganic core models of WOC [37, 38] and nitrogenase [39] from simple ions in water even in the
absence of any amino acids. Image from ref. [39].
For example, manganese oxides have been reported as heterogeneous catalysts for water oxidation [41]. Interestingly,
Najafpour et al. have shown that the incorporation of calcium ions into manganese oxides can improve the catalytic
activity of synthetic manganese oxides [37, 38]. In addition to these calculations, Siegbahn showed that there is great
similarity between manganese-calcium oxides and manganese-calcium clusters in water oxidation in Photosystem II
[57]. Siegbahn used a hypothetical Mn-O crystal constructed with all Mn-Mn distances set to 2.70 Å and all Mn-O
distances set to 1.90 Å. In the next step, one calcium atom was inserted into the surface of this crystal, with all Ca-Mn
distances equal to 3.4 Å and all Ca-O distances set to 2.4 Å. These distances are very similar to the ones in the manganese
calcium cluster in Photosystem II (Fig. 25.4). This comparison also shows similarity between the inorganic cofactor of
enzymes and metal oxides [57].
In another report, Dörr et al. described a method for the synthesis of ammonia from dinitrogen using H
2
S as a reductant and
iron sulfide, which could be considered an inorganic core for the nitrogenase [44]. The reductant, as well as the reaction condi-
tions (atmospheric nitrogen pressure and temperatures on the order of 70-80°C), is rather mild and comparable to biological
processes [44]. Other models are shown in Table 25.1.