Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
O
O
C
KH 570
H
2
AA/AN
OH
O
Si
O
C
CH
2
CH
3
C
3
DMF/H
2
O
O
AT P
ATP-KH 570
O
O
C
C
H
2
NH
2
OH
2
HCl/Na
2
CO
3
H
2
O
Si
O
3
H
2
O
H
2
H
H
2
H
O
C
C
C
C
m
n
CH
3
COOH
CN
P(A-N)/AT
O
O
H
2
O
Si
O
C
3
H
2
H
2
H
2
H
H
O
C
C
C
C
C
C
m
n
C
CH
3
COONa
H
2
N
NOH
P(A-O)/AT
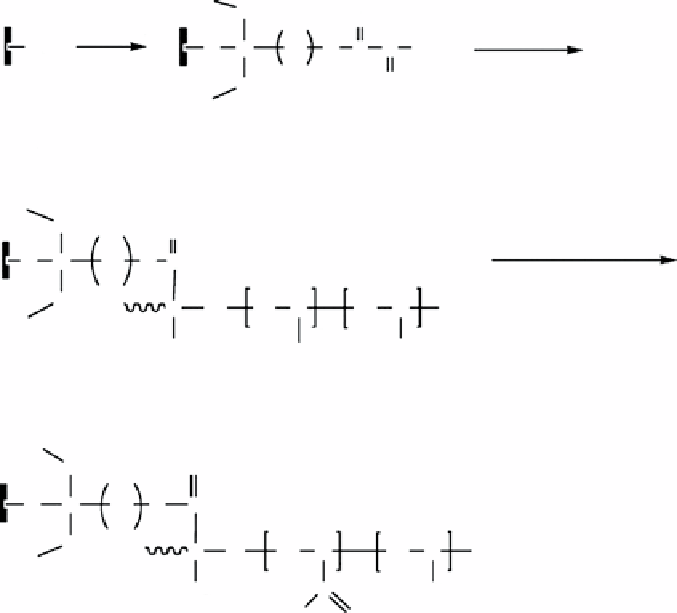
figure 16.16
scheme for the preparation procedure to P(A-O)/AT.
A novel amphiphilic hybrid material ATP-P(s-b-dVB-g-AO) (AsdO) was synthesized via the combination of sI-ATRP and
radical grafting polymerization, after transforming An units into acrylamide oxime (AO) as a hydrophilic segment (fig. 16.17)
[95]. The amphiphilic hybrid material was employed in the absorption of heavy metal and organic pollutants. The adsorption
capacity of AsdO for Pb(II) was 131.6 mg/g, and the maximum removal capacity of AsdO toward phenol was found to be
18.18 mg/g in the case of monolayer adsorption at 30°C. The optimum pH was 5 for both lead and phenol adsorption. desorption
of the adsorbed contaminants from AsdO can take place in alkali solution (1 mol/l naOH). Repeating the test for six times
revealed that the synthesized hybrid materials maintained the stable high adsorption capacity during the adsorption/desorption.
Previous research works suggest that chemically modified clay minerals with small organic molecules or polymers present
a new and promising class of adsorbents for water purification and industrial wastewater treatment, especially for the adsorption
of metal ions from aqueous solutions [96]. It has been found that these clay minerals would have as great an efficiency as
activated carbon if the difficulty experienced in the recovery of the adsorbent from filters after use could be overcome. This also
makes the regeneration and possible reuse of a clay adsorbent very difficult.
unuabonah et al. synthesized a novel water-stable ion exchange resin for the adsorption of metal ions with polyvinyl alcohol
(PVA) kaolinite clay as a PVA-nanoclay adsorbent, in order to address the problem of the recovery of adsorbent/resin from
filters after use [97]. This adsorbent was found to have an adsorption capacity of 56.18 mg/g for Pb
2+
ions and 41.67 mg/g for
Cd
2+
ions. The adsorption data obtained was well explained by the diffuse Layer model (dLm), which implies that the adsorp-
tion of both metal ions onto the modified adsorbent was via an inner-sphere surface complexation mechanism. Virtually
complete desorption (ca. 99%) of both metal ions occurred from the PVA-nanoclay within 3 min.
16.4
COnClusiOns and PrOsPeCts
The organo-clay nanohybrid adsorbents have been investigated intensively particularly in the removal of a variety of toxic HmI
from water. The clay minerals functionalized with organo-compounds become more hydrophobic with enhanced interspace
basal spacing, enabling enhanced and selective affinity toward inorganic oxyanions/cations. Although these materials possess