Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
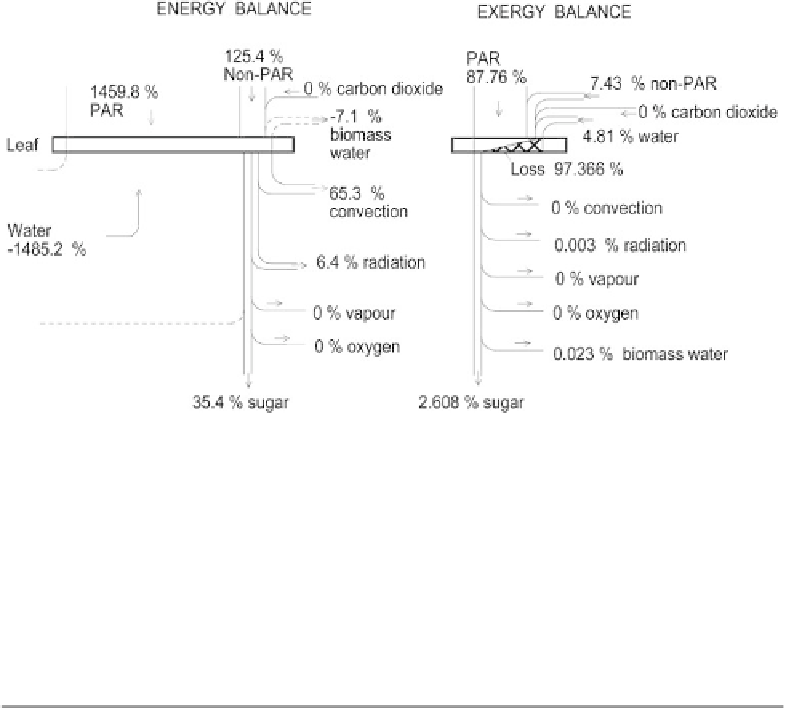
Figure 2.4.20
Band diagram of energy and exergy balances for the considered photosynthesis process
shown in Figure 2.4.19 (from Petela, 2010).
external side of the system boundary layer, have the parameters equal to the environ-
ment parameters. The exergy of convective heat is zero because it is released to the
environment. The exergy of the leaf radiation (0.003%) is small due to relatively low
temperature of the leaf and is significantly smaller than the respective energy (6.4%).
The exergy of liquid water contained in the produced biomass is 0.023%, (positive).
Unlikely the enthalpy and energy analyses, exergy analysis shows the irreversibility
loss, which in this case is relatively very large (97.366%).
More aspects of the energy and exergy balances and some inspired problems were
analyzed by Petela (2010).
2.4.5 Photovoltaic
The present paragraph gives an outline of the simple energy and exergy analysis of
the simultaneous generation of heat and power by photovoltaic (PV) technology. This
double conversion of radiation energy can categorize the PV technology into the general
systems of cogeneration of power and heat.
In the considerations only direct solar radiation is accounted for the case of a
clear sky (at temperature
T
sky
assumed as environment temperature
T
0
,
T
sky
=
T
0
),
and assuming the Sun is a black surface. As there is no motion of substance in the
gravitational field, the eZergy consideration is not introduced. The 1 m
2
surface of a
solar cell at temperature
T
C
is shown in Figure 2.4.21. Generally, the heat
q
S
transferred
from the Sun's surface at temperature
T
S
to the outer surface of the solar cell on
the Earth is distributed to the generated electrical energy
E
, reflected solar radiation
q
r
, useful heat
q
C
absorbed by the solar cell, and to convection and radiation heat
Search WWH ::

Custom Search