Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
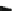
Fig. 3 Mie scattering for
particles with diameter
d ¼
10 l, where l is the light
wavelenght
90
120
60
150
30
0
180
210
330
300
240
270
i.e., the receiving optics is placed at an angle larger than 90
from the transmitting
optics.
The receiving optics collects the light scattered by the particles in the measuring
volume and conveys it to the photodiode. The diameter of the tracer particles is
larger than the wavelength of the laser light. Light scattering is thus said to be in
the Mie regime (Albrecht et al.
2003
). A typical light scattering diagram is shown in
Fig.
3
. As shown in the figure, the forward direction is the most effective. LDA
systems operating in the forward scatter mode are, however, not dominant, for
constructive and operative reasons. Systems operating in backscattering systems
have the receiving and the transmitting optics in one single probe, with the former
optics focused by the manufacturer. In the forward scatter mode, the user is
generally required to place and to focus the receiving optics, introducing extra
source of measurement errors.
The Doppler principle by which the LDA operates is better explained with what
is called the fringe model. Figure
4
illustrates the main principles. A fringe pattern
is originated when two monochromatic (same wavelength) coherent (same phase
for all waves) light beams are superimposed. Where the interfering light is in phase
a peak (bright fringe) is generated; where it is out of phase, light is canceled out and
a trough (dark fringe) occurs. In the LDA case, this fringe pattern occurs in the
measurement volume. The fringe pattern is parallel to the axis of the transmitting
optics.
The spacing between fringes depends on the wavelength of the crossing beams,
l, and on the angle that they form, y. Simple geometrical considerations (Fig.
4
)
lead to the formula:
l
d
¼
(1)
2 sin
ð
y
=
2
Þ
A particle crossing the control volume with velocity
u
normal to the axis of the
probe will generate a burst which, in the time domain, is a wave packet with frequency
f