Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
Fig. 1 General layout of an LDA system (Adapted from Dantec Dynamics LDA literature
http://
www.dantecdynamics.com/Default.aspx?ID
¼
1046
)
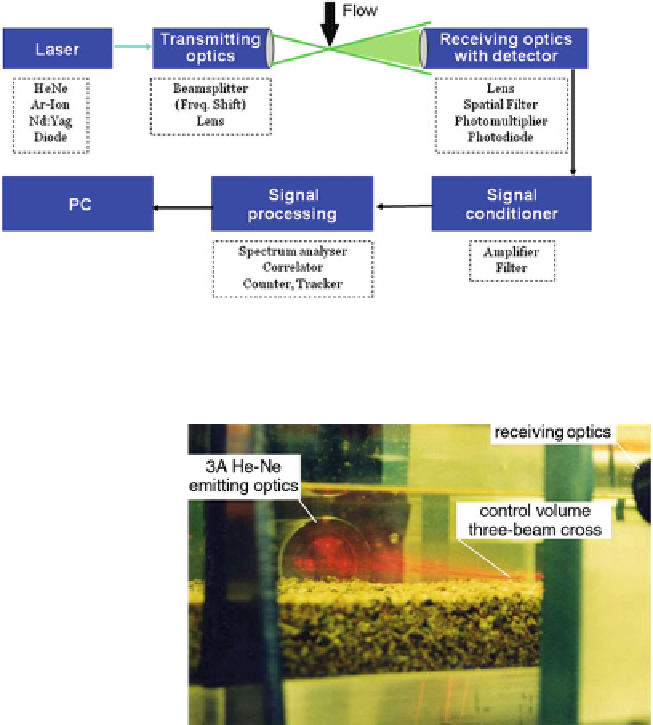
Fig. 2 A 3A He-Ne LDA,
in foward scattering mode,
measuring over a gravel
bed (From Ferreira
2005
)
spectra or Neodymiumdoped Yttrium Aluminum garnet (Nd:Yag). The former two
are gas-lasers, i.e., coherent light produced by the excitation of a gas by a strong
electric current. The latter is a solid-state laser, in which a crystalline medium is
modified (doped) with small concentrations of impurities to change its electrical
properties; the crystalline medium is optically excited (optically pumped, generally
by diode lasers) to produce population inversion and, hence, emission of photons
(Csele
2004
).
The laser beam is split before reaching the transmitting optics. A Bragg cell is
normally used for beam splitting and also to ensure that directional ambiguity is
eliminated (see Fig. 5 below). The beams are focused in the transmitting optics in
order to intercept in a measurement volume. One pair of beams of a given wave-
length is necessary to measure one velocity component. Figure
2
shows a two-
component He-Ne LDA system where two pairs of 632.8 nm laser beams intercept
above a gravel bed. The system in Fig.
2
is operated in forward scattering mode,