Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
an irreducible cost. An optimum design would minimize the ratio of cost to heat collection and
would have an area intermediate between a small and large value because these extremes have
either small heat collection or large cost, making the ratio larger than the optimum.
7.5.2
Focusing Collectors
The purpose of employing focusing solar collector systems is to increase the intensity of the solar
radiation falling on the collector, thereby making it possible to collect solar energy at a higher
temperature and with a smaller collector area than for a simple flat plate system. The factor by
which the solar irradiance is increased is called the concentration ratio,
CR
.
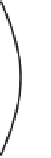
The principle of light concentration is sketched in Figure 7.9. A curved parabolic mirror whose
axis points in the sun's direction will form an image of the sun at its focal point, a distance
F
from
the mirror called the focal length. The image dimension
D
i
is equal to the product of the focal
length
L
and the small plane angle
radian that the sun subtends when viewed from
the earth. The ratio of mirror dimension
D
m
to image dimension
D
i
is thus found to be
α
=
9.3E
(
−
3
)
D
m
D
i
=
D
m
α
5
D
m
F
F
=
107
.
(7.5)
For an ordinary mirror of circular shape that forms an image as does a camera (called spherical), the
concentration ratio is equal to the ratio of the area of the mirror to that of the image, or
2
.
For a cylindrical mirror, which focuses light only in one dimension, the concentration ratio is
(
(
D
m
/
D
i
)
D
m
/
D
i
)
. Thus
D
m
F
2
CR
=
1
.
156E
(
4
)
(
spherical
)
D
m
F
=
1
.
075E
(
2
)
(
cylindrical
)
(7.6)
In camera lenses, the ratio of focal length to lens diameter is called the
f number
. The smaller its
value, the greater is the lens' light gathering power, or concentration ratio, permitting film exposure
in dim lighting conditions. For focusing solar collectors, it is not practical to construct mirrors with
F
D
m
less than about 2.
The collectors for focusing systems, which operate at higher temperatures, are of different
design than those for flat plate systems. Nevertheless, their collection efficiency and maximum
/
Collector
Mirror
D
m
D
i
I
F
Figure 7.9
A focusing mirror
(
D
m
)
concentrates the solar irradiance
I
(dashed lines) on a smaller collector
(
D
i
)
located at the focal point of the mirror.