Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
Push
sampling
Piston
sampling
Ambient
pressure
sampling
CPT/CPTU
seismic CPTU
Elec. cond. CPT
Heat
flow
data
In situ
vane
CPTU
permea-
meter
Dilato-
meter
(NGI)
Bat-
probe
(NGI)
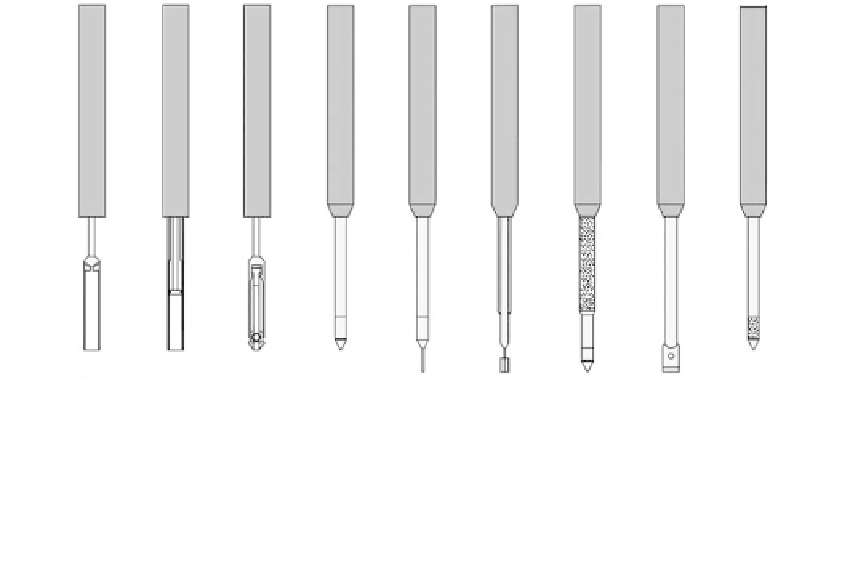
FIGURE 2.43
Various sampling and
in situ
testing tools used with the Fugro Seaclam (see
Figure 2.42
).
BAT probe is an
electrical resistance piezometer. (Courtesy of Fugro.)
Permit
in situ
measurements of the physical and engineering properties of the
materials
●
Obtain information on groundwater conditions
●
Boring Types
They may be classified according to sampling operations:
Wash sample borings
are made to recover completely disturbed samples for
general classification only.
●
Sample borings
are made to recover partially disturbed samples (SPT) or undis-
turbed samples (UD).
●
Core borings
are made to recover rock cores.
●
Rotary probes
recover only rock cuttings and are made to provide a rapid deter-
mination of the bedrock depth.
●
Air track probes
result in rock cuttings at the surface and are made to provide a
rapid determination of rock quality.
●
Operational Elements
The execution of a boring requires fragmentation of materials, removal of the materials
from the hole, and stabilization of the hole walls to prevent collapse.
Fragmentation
Materials in the hole are fragmented for removal by:
Circulating water in loose sands or soft clays and organic soils
●
Chopping while twisting a bit by hand (wash boring), or rotary drilling or auger-
ing in moderately strong soils
●