Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
tion. The next steps include implementing and field-testing the controller in the prototype
turbine. The controller must be tested in the field for a variety of wind and operating condi-
tions. The whole process from start to finish may need to be repeated in order to optimize the
controller for the final wind turbine design.
Simulation Tools
NREL researchers have documented the use of control design tools based on the FAST
code [Wright and Fingersh 2008], providing demonstrations of available control design and
simulation tools. Various advanced control design methods are also discussed in this report,
based on full state feedback, state estimation, DAC, and LQR.
Testing the controller through simulation can be a challenging step. The control design
must be tested under a broad range of simulated wind and turbine operating conditions. This
necessitates the generation of
turbulent wind input cases
that represent the unsteady winds
at a selected site, using specialized codes such as TurbSim [Jonkman and Buhl 2007]. Sto-
chastic inflow codes of this type simulate full-field flows that contain coherent turbulence
structures, with the space and time relationships seen in instabilities associated, for example,
with nocturnal boundary layer flows
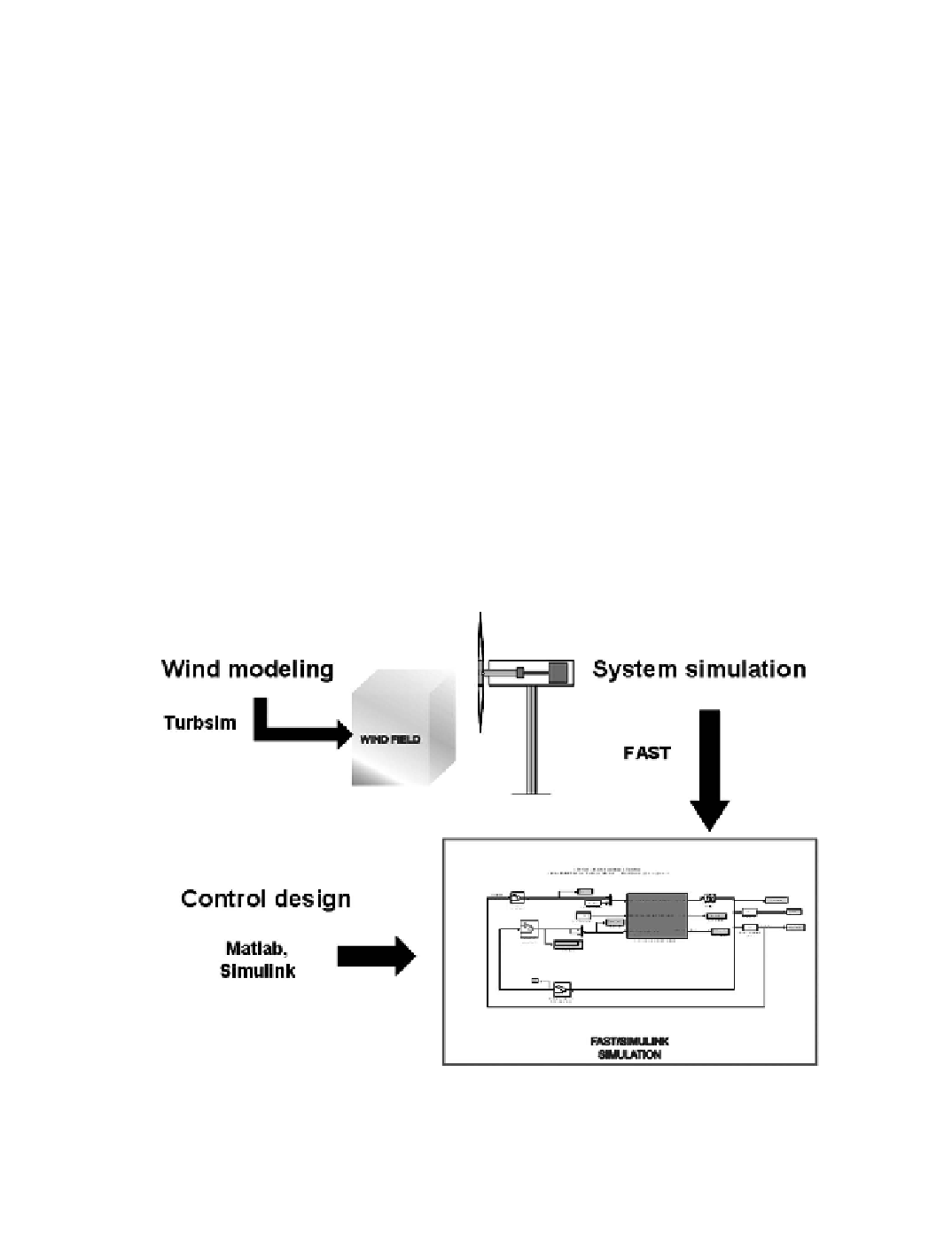
Another software tool that was developed to test turbine controls is illustrated in Figure
14-6. This tool is an interface developed between NREL's FAST wind turbine simulation
code [Jonkman and Buhl 2005] and SIMULINK [Grace
et al
. 1992], a popular simulation
tool for controls design. This combination introduces tremendous flexibility in wind turbine
controls implementation during simulation. Generator torque control, nacelle yaw control,
and blade pitch control modules can all be designed in the SIMULINK environment and
simulated while making use of the complete nonlinear aeroelastic wind turbine equations of
motion available in FAST.
Figure 14-6. Schematic diagram of the application of NREL's advanced software tool,
FAST/SIMULINK Simulation, combining control design and system simulation, in-
cluding modeling of wind inputs with TURBSIM.
Search WWH ::

Custom Search