Global Positioning System Reference
In-Depth Information
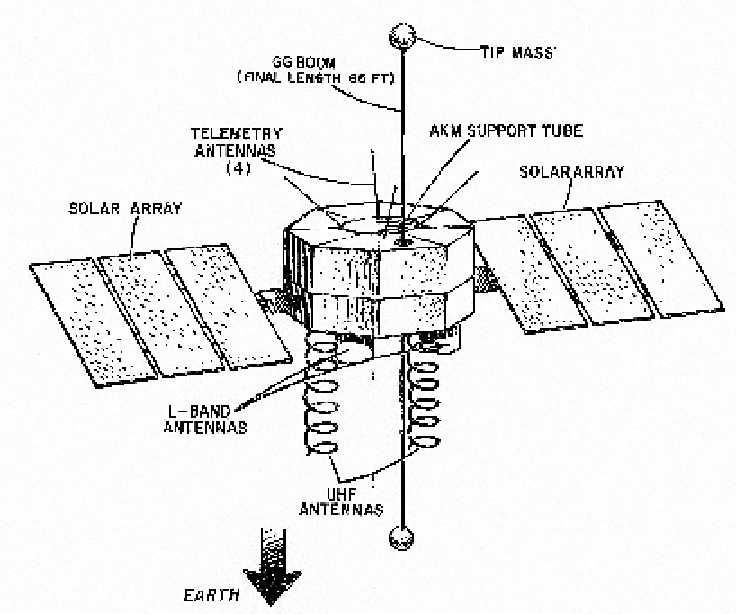
Fig. 4.5. Diagram of nts- 2 satellite. nts-2, the final nrl navigation satellite, carried the
first cesium atomic clock into orbit in 1977. (Courtesy Naval Research Laboratory)
recent test which synchronized the NavStar inverted range at Yuma Washing-
ton with the orbiting Navigation Technology Satellite (nts-2). This constituted
the first true navigational test of the NavStar-gps concept, using a satellite and
proved that the system is a workable one, according to officials from the joint
program office at Air Force Space and Missile Systems Organization (samso).”
32
Harvard professor Peter Galison has written that Einstein's development of
special relativity was at least partially inspired by observing synchronized clocks
of worldwide clock synchronization. nrl's Vince Folen and Don Lynch esti-
mated correctly the relativistic corrections used in nts-2's cesium clocks and
University of Maryland professors Joe Weber and Carroll Alley were also very
helpful in this calculation. The nrl's Peter Wilhelm and his staff built all four
Timation satellites and developed innovative techniques to minimize launch
costs. The 1971
Timation Development Plan
proposed launching all twenty-
seven satellites using three rockets with an estimated completion date of 1984.
After receiving approval in December 1973, Parkinson and the jpo imple-
Search WWH ::

Custom Search