Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
West Germany to the unifi ed Germany. As we see today, this was a clever move.
According to the statistics, there was a 17% reduction in CO
2
emissions by 2005.
As a result, Germany likes to present itself as a forerunner in climate protection on
the international stage. However, most of the CO
2
savings can be attributed to the
effects of reunifi cation. A major part of the industry in the former East Germany,
with its high level of energy consumption and carbon dioxide emissions, collapsed.
The output of greenhouse gases was thereby reduced to around half of what it had
been, whereas in West Germany nothing much was changing in terms of climate
protection.
After the change in government in 1998, the 'Red-Green' government, a coalition
between the Green Party and Social Democrats, also adopted the climate protection
targets for the year 2050. However, the measures introduced were not adequate for
an effective climate protection policy that would make the targets realistic. The fi rst
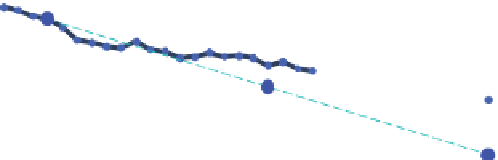
target of a 25% reduction by 2005 was missed by a long shot (Figure 2.12). Even
the current German government is not moving ahead quickly enough to reduce
greenhouse gas emissions.
reference year 1990
goal -25 %
goal-50 %
1200
Mt
total Germany
1000
Kyoto goal
800
trend
Western Germany
trend
600
goal
400
goal
200
goal
Eastern Germany
trend
0
1985
1990
1995
2000
2005
2010
2015
2020
Figure 2.12
Energy and process-related carbon dioxide emissions in Germany.
On the international stage Germany had already qualifi ed its climate protection
targets in 1997. Under Angela Merkel, the environmental minister at the time, the
government's own target was a reduction of 25% by 2005. Within the framework
of the Kyoto Protocol, a reduction target for greenhouse gases of only 21% was
promised by the year 2012. In addition to carbon dioxide, the calculations of the
Kyoto protocol take into account other climate gases, such as methane, nitrous
oxide, HFC and CFCs. This clearly improves Germany's chances of at least reach-
ing the Kyoto target. It has had great success particularly in the reduction of methane
emissions - for example, through recycling.