Civil Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
load-slip behavior of the connector was also of equal importance. The slip
at the steel-concrete interface depends on many factors such as type of con-
nector, size of shear connector, spacing between connectors, type of floor
slab, and concrete strength of slab. To evaluate the load-slip behavior of
the connector taking into account all parameters that affect the shear con-
nection, an unlimited number of expensive push-off tests would need to
be carried out. Numerical modeling of push-off tests can be used in carrying
out extensive parametric studies to evaluate the load-slip behavior of the
shear connector.
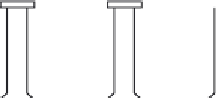
The development of the electric drawn arc stud welding apparatus in
1954 allowed a type of shear connector known as the headed stud connector
(see
Figure 2.14
)
to be rapidly fastened to the top flange of the steel beams
in situ
. Due to its advantages over other forms of shear connection, such as
rapid installation and the fact that they were equally strong and stiff in shear
in all directions normal to the axis of the stud, the stud connector became
one of the most popular types of connector used in composite construction.
Studies of stud connectors did not begin until 1956. Push-off tests on stud
studs with an upset head of diameter ranging from 0.5 (13 mm) to
1.25 in. (32 mm). Fatigue and static tests were also performed by Thurli-
studs and, to a lesser extent, 0.75 in. (19 mm) diameter straight studs with
an upset head. All the push-off tests showed that steel studs are suitable
for use as shear connectors and that the behavior of a stud connector is similar
to that of a flexible channel connector. The shear capacity was found to be a
function of the diameter and height of the stud and of the strength of the
concrete.
During the latter half of the 1950s, profiled steel sheeting (decking) (see
Figure 2.15
)
was introduced in the North American steel construction
Not less than 1.5 d
Auto
matic stu
d weld
d
20 mm min.
Figure 2.14 Headed stud shear connector.
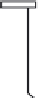























Search WWH ::

Custom Search