Civil Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
8
7
5
6
y
4
3
1
z
2
x
Figure 5.5 CAXA8R axisymmetric solid elements.
deformation (AXA) having eight (8) nodes with reduced (R) integration as
shown in
Figure 5.5
.
Stress/displacement axisymmetric solid elements with-
out twist have two active degrees of freedom per node.
Reinforcement bars and prestressing tendons are commonly modeled in
general-purpose software as “embedded” uniaxial (1D) finite elements in the
form of individual bars or smeared layers. As an example in ABAQUS [1.29],
reinforcement bars and prestressing tendons are included in the “host” ele-
ments (concrete elements) using the REBAR option. The option is used to
define layers of uniaxial reinforcement in membrane, shell, and solid ele-
ments. Such layers are treated as a smeared layer with a constant thickness
equal to the area of each reinforcing bar divided by the reinforcing bar spac-
ing. The option also can be used to add additional stiffness, volume, and mass
to the model. In additions, it can be used to add discrete axial reinforcement
in beam elements. Embedded rebars can have material properties that are
distinct from those of the underlying or host element. To define a rebar
layer, modelers can specify one or multiple layers of reinforcement in mem-
brane, shell, or solid elements. For each layer, modelers can specify the rebar
properties by including the rebar layer name; the cross-sectional area of each
rebar; the rebar spacing in the plane of the membrane, shell, or solid element;
the position of the rebars in the thickness direction (for shell elements only),
measured from the midsurface of the shell (positive in the direction of the
positive normal to the shell); the rebar material name; the initial angular ori-
entation, in degrees, measured relative to the local 1-direction; and the iso-
parametric direction from which the rebar angle output will be measured.
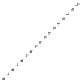
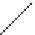
Figures 5.6-5.8
show examples of reinforcement bars imbedded in different
finite elements as presented in ABAQUS [1.29].












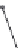























Search WWH ::

Custom Search