Civil Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
r¼
l
p
0
:
188
l
p
>
1
:
0 for
0
:
748
l
p
where
s
f
y
s
cr
b
=
t
l
p
¼
¼
4
e
p
ð
3
:
54
Þ
28
:
k
s
where
c
is the stress ratio used in Tables 4.1 and 4.2,
b
is the appropriate
width, and
k
s
is the buckling factor corresponding to the stress ratio
c
and boundary conditions. For long plates,
k
s
is given in Table 4.1 or
critical plate buckling stress, and
e ¼
235
1, a column type of buckling
may occur (see
Figures 3.24
and
3.25
)
, and the check should be performed
<
b
a
Figure 3.24 Definition of aspect ratio
a¼a/b of rectangular plates.
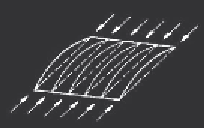
Column-like behavior of plates
without longitudinal supports
Column-like behavior of an unstiffened
plate with a small aspect ratio
a
(b)
(a)
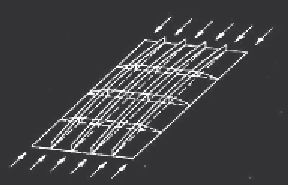
Column-like behavior of a longitudinally
stiffened plate with a large aspect ratio
a
(c)










Search WWH ::

Custom Search