Java Reference
In-Depth Information
If a table is no longer needed, it can be dropped permanently using the
drop table
com-
mand. For example, the following statement drops the
Course
table:
drop table
Course;
drop table
If a table to be dropped is referenced by other tables, you have to drop the other tables
first. For example, if you have created the tables
Course
,
Student
, and
Enrollment
and
want to drop
Course
, you have to first drop
Enrollment
, because
Course
is referenced by
Enrollment
.
Figure 32.10 shows how to enter the
create table
statement from the MySQL console.
F
IGURE
32.10
A table is created using the
create table
statement.
If you make typing errors, you have to retype the whole command. To avoid retyping, you
can save the command in a file, and then run the command from the file. To do so, create a
text file to contain commands, named, for example,
test.sql
. You can create the text file using
any text editor, such as Notepad, as shown in Figure 32.11a. To comment a line, precede it
with two dashes. You can now run the script file by typing
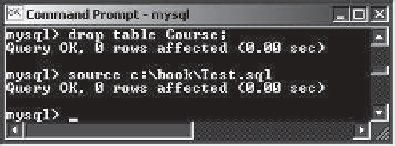
source test.sql
from the SQL
command prompt, as shown in Figure 32.11b.
(a)
(b)
F
IGURE
32.11
(a) You can use Notepad to create a text file for SQL commands. (b) You
can run the SQL commands in a script file from MySQL.
32.3.4 Simple Insert, Update, and Delete
Once a table is created, you can insert data into it. You can also update and delete records.
This section introduces simple insert, update, and delete statements.
The syntax to insert a record into a table is:
insert into
tableName [(column1, column2, ..., column)]
values
(value1, value2, ..., valuen);

















Search WWH ::

Custom Search