Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
pf
X|1
qf
X|−1
qf
X|−1
pf
X|1
x
0
x
0
x
0
−
δ
x
0
−
δ
(a)
(b)
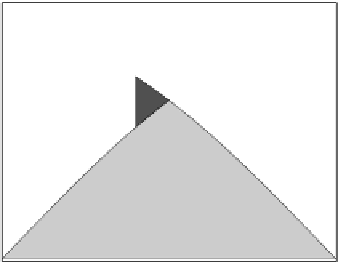
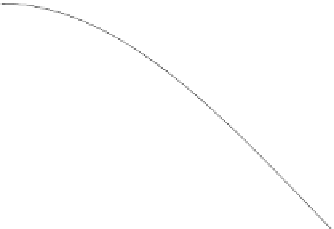
Fig. 4.1 The two intersection cases of
qf
X|−
1
and
pf
X|
1
. The light shadowed areas
correspond to
P
e
(
x
0
)
. The dark shadowed area is the amount of error probability
added to
P
e
(
x
0
)
when the split point moves to
x
0
− δ
. The dashed area is the
amount of error probability subtracted from
P
e
(
x
0
)
when the split point moves to
x
0
− δ
.
P
e
(
x
)=
x
−∞
pf
X|
1
dx
+
+
∞
x
qf
X|−
1
dx.
(4.8)
If there is no intersection of
qf
X|−
1
with
pf
X|
1
,thenmin
P
e
=min(
p, q
)
≤
1
/
2
occurs at +
.
For intersecting posterior densities, one has to distinguish two cases. First,
assume that for
δ>
0
∞
or
−∞
pf
X|
1
(
x
)
<qf
X|−
1
(
x
)
x
∈
[
x
0
−
δ, x
0
]
(4.9)
pf
X|
1
(
x
)
>qf
X|−
1
(
x
)
x
∈
[
x
0
,x
0
+
δ
]
,
(4.10)
where
x
0
is an intersection point of
qf
X|−
1
with
pf
X|
1
as illustrated in
Fig. 4.1a.
The probabilities of error at
x
0
and
x
0
−
δ
are
P
e
(
x
0
)=
p
x
0
−δ
−∞
f
X|
1
(
x
)
dx
+
q
+
∞
x
0
f
X|
1
(
x
)
dx
+
x
0
x
0
−δ
f
X|−
1
(
x
)
dx,
(4.11)
P
e
(
x
0
− δ
)=
p
x
0
−δ
−∞
f
X|
1
(
x
)
dx
+
+
q
x
0
x
0
−δ
f
X|−
1
(
x
)
dx
+
+
∞
x
0
f
X|−
1
(
x
)
dx
.
(4.12)
Hence,