Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
1.2.1 Permanent-Magnetic Synchronous-Generator
The PMSG was represented by the following equations [
1
]:
1
x
b
dw
ds
dt
¼
v
ds1
þ
R
s
i
ds
þ
x
e
w
qs
ð
1
:
1
Þ
dw
qs
dt
1
x
b
¼
v
qs1
þ
R
s
i
qs
x
e
w
ds
with
w
ds
¼
L
ds
i
ds
w
m
;
w
qs
¼
L
qs
i
qs
ð
1
:
2
Þ
where v is the voltage, R is the resistance, i is the current, x
e
is the stator electrical
angular speed, x
b
is the base angular speed in rad/sec, L
s
is the stator leakage
inductance, w
m
is the exciter flux of the PMSG, and w is the flux linkage. The
subscripts d and q indicate the direct and quadrature axis components, respec-
tively. The subscripts s and 1 indicate stator quantities and bus 1 shown in Fig.
1.1
,
respectively. The electrical active and reactive power delivered by the stator are
given by
P
s
¼
v
ds1
i
ds
þ
v
qs1
i
qs
;
Q
s
¼
v
ds1
i
qs
v
qs1
i
ds
ð
1
:
3
Þ
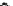
The mathematical model of a TL, a TR, a cable, and a load can be obtained
from the description of the R, L, C segment [
20
] into the dq-synchronous reference
frame. The equations of the TL, the TR, the cable, and the RL load are given in
Eqs.
1.4
-
1.7
based on Fig.
1.3
where superscripts s and e stand for the sending-
end and the receiving-end.
s
ω
e
Li
q
l
i
d
i
dc
e
i
d
l
R
L
i
d
+
+
s
e
i
dc
s
e
v
d
v
d
s
ω
e
Cv
q
e
C
ω
e
Cv
q
C
_
_
s
e
i
q
i
ql
ω
e
Li
dl
L
i
q
R
+
+
s
e
i
qc
i
qc
s
e
v
q
v
q
e
s
ω
e
Cv
d
C
ω
e
Cv
d
C
_
_
Fig. 1.3
Lumped-parameter p equivalent-circuit description in the dq-domain