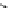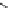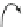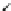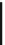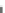Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
PMSG-WT
2
PMSG-WT
1
PMSG-WT
5
...
1
1
1
0.69
/22.9kV
0.69
/22.9kV
0.69
/22.9kV
TR
TR
TR
2
2
2
Ca
2km
4
(PCC)
22.9
/154kV
5
3
14km
TR: Transformer
TL: Transmission line
Ca: Cable
IB: Infinite bus
PCC: point-of-common coupling
TL
TR
IB
Local load
Fig. 1.1
Grid-connected wind turbine system
Wind
speed
v
wt
Generator-side
converter
Grid-side
converter
1
Driv
e
train
DC-link
Filter
PMSG
ω
t
P
s
P
g
P
m
Rotor blade
& pitch control
VSC
controller
(Fig. 4)
v
dq,s
v
dq,g
Fig. 1.2
Permanent-magnetic synchronous generator wind turbine (PMSG-WT)
and tower require extensive knowledge of aerodynamics, mechanical and struc-
tural engineering, control and protection of electrical subsystems, etc.
The details of the WT considered in the model are shown in Fig.
1.2
. The WT
consists of the following components: a three-bladed rotor with the corresponding
pitch controller [
17
]; a PMSG with two converters, a dc-link capacitor, a grid filter;
and converter controllers.
The generator parameters of a 2 MW PMSG-WT can be found in [
1
]. The
electrical part of the overall system is modeled using the dq-synchronous reference
frame [
18
,
19
] representation of the individual components. Wherein, the d-axis is
assumed to be aligned to the stator flux, and the current coming out of the machine
is considered positive. The PMSG controllers utilize the concept of disconnection
of the active and reactive power controls by transformation of the machine
parameters into the dq-reference frame and by separating forming of the stator
voltages. Then, the active power can be controlled by influencing the d-axis
component of the stator current while the reactive power can be controlled by
influencing the q-axis components of the stator current. The system parameters and
control gains, etc., are summarized in the Appendix.