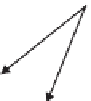Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
&HQFKUXVFLOLDULV
,QGXFHGVFOHULILFDWLRQLQ
YDVFXODUUHJLRQ
&\QRGRQGDFW\ORQ
'LVLQWHJUDWLRQRIFRUWLFDO
SDUHQFK\PD
&\QRGRQGDFW\ORQ
)RUPDWLRQRIFU\VWDOVLQ
SDUHFK\PDWRXVUHJLRQ
&\SHUXV DORSHFXURLGHV
6FOHULILFDWLRQQ
K\SRGHUPDOUHJLRQ DQG GHYHORSPHQW RI
VWHOODWHSDUHQFK\PD
&\QRGRQGDFW\ORQ
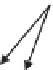
6FOHULILFDWLRQLQYDVFXODU
UHJLRQGHSRVLWLRQRI1LLQHSLGHUPDODQG
FRUWLFDOUHJLRQ
&\QRGRQGDFW\ORQ
'HSRVLWLRQRI &GQ
FRUWLFDOUHJLRQ
+HOLDQWKXVDQQXXV
'DPDJHRI HSLGHUPDO
KDLUGHSRVLWLRQRI1LLQVWHPKDLU
+HOLDQWKXVDQQXXV
'HSRVLWLRQRI&GLQVWHP
KDLU
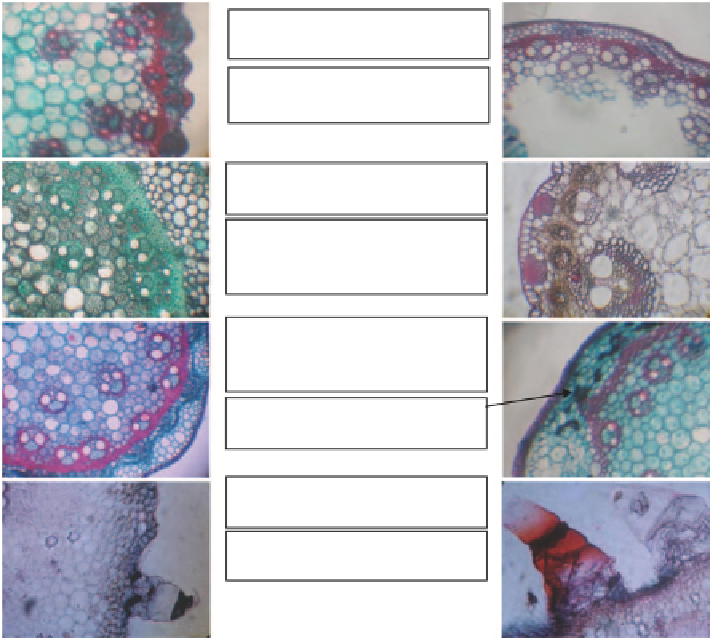
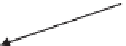
Fig. 5.2
Influence of heavy metal stress on stem anatomy of some selected plant species
3.3.2
Stem Anatomy
Stem tissue organization can be severely affected due to heavy metal toxicity
(Fig.
5.2
). Setia and Bala (
1994
) reported disorganization of epidermal cells, dis-
integration of root cortical cells and a reduction in cell wall thicknesses of epi-
dermis and hypodermis as a result of Ni toxicity. Sresty and Rao (
1999
) observed
a reduction in stem diameter, vascular bundle number and cell size of storage
regions under Ni toxicity. In contrast, Kasim (
2006
) reported a significant reduc-
tion in root diameter, but not in stem diameter when plants were exposed to Cu
and Cd stress.
de Silva et al. (
2012
) studied the effects of heavy metal stress on xylem char-
acteristics in
Acer rubrum
and reported a reduction in the proportion of xylem
tissue. Diameter and density of xylkem vessels also reduced significantly. The
reduction in vessel size may result in reduction in hydraulic conductance in both
root and shoot.