Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
(a)
Bit failure rate (log scale).
(b)
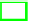
Useful capacity
Fig. 5.
Bit Failure Rate due to scaling voltage and he Useful cache capacity provided
by Flexicache after disabling uncorrectable lines under this bit failure rate
5 Evaluation
In this section, we compare Flexicache against a conventional triplication scheme
(TMR) and MS-ECC [12]. We use 4-way set associative, 64KB L1 cache with
2-cycle access time, 64B line size. We divide each line into 32 partitions for both
OLSC and Flexicache with the partition size of 16 bits.
Miller et al [23] examined the persistent bit failure rate in the given
V
dd
for
32nm technology (Figure 5a). As
V
dd
is lowered, the bit failure rate increases
exponentially. Flexicache targets to tolerate ultra high bit failure rates occur-
ring in the near-threshold voltage level without harming the performance of the
cache in the low error rate. For the calculation of the
V
dd
that Flexicache oper-
ate reliably, we reference these previous results. We inject persistent faults into
random locations according to bit failure rate (i.e. probability that a single bit
fails) given in [23]. We calculate the useful cache capacity as the portion of the
cache which is not disabled. For non-persistent failure such as soft errors, we in-
ject multi-bit failures varying between 1 to 10 bits. We present the experimental
results for the aspects of 1) useful cache capacity, 2) error correction latency, 3)
energy reduction of cache operations, and 4) reliability against non-persistent
faults (mean time to failure) and 5) uniform view of the cache. 6) area overhead,
Useful Cache Capacity:
Figure 5b compares the cache capacities. We ex-
tend Flexicache with extra slices in order to make it divisible to three, and
we normalized the useful cache capacity to the non-extended capacity for fair
comparison. First, when the
V
dd
is high, Flexicache do not sacrifice the useful
cache capacity due to its flexible circuit design which dynamically switch its
configuration to 64KB general purpose data cache (i.e. SVM). Second, due to
the partitioning and partition-fix mechanism of Flexicache, it provides higher
cache capacity than the conventional triplication schemes even in the low-power
mode. Third, Flexicache can operate until the persistent bit failure rate is 12%
while TMR can operate until 6% bit failure rate and MS-ECC can operate