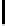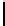Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
Table 2.
The figure analysis the area overhead and latency
Flexicache
MS-ECC
Encoder
Decoder
Encoder
Decoder
Number of Gates in
4XORs 7XORs+ 2XORS 2XORs+
the Critical Path
2 ANDs +
2 ANDs +
2ORs
4ORs
Total Number
480 XORs 3K XORs + 1,5K XORs 6K XORs +
of Gates
1,5K ORs +
4,5K ORs +
3,5K ANDs
10K ANDs
Latency
1cycle
1cycle
1cycle
1cycle
Energy Overhead
2,5%
20%
5,5%
50%
(In the nominal voltage)
Area Overhead
0.06%
0.12%
(Encoder+Decoder)
until 2% bit failure rate (Bit failure rates are not shown in the graph). There-
fore, TMR and MS-ECC can provide more more than 20% of the cache capacity
when the supply voltage is as low as 400mV while Flexicache can provide the
similar amount of useful cache capacity when the supply voltage is 320 mV.
Error Correction Latency:
In Table 2, we compare the area overhead and
the latency presented by encoders and decoders in Flexicache and OLSC. We
first present the number of gates in the critical paths. Although, in Flexicache,
the number of gates in the critical path are higher than the one in MS-ECC, both
encoding and decoding in each scheme can be accomplished in 1 cycle. Note that
the decoding latency can be tolerated since decoding is done simultaneously with
writing. On the other hand, total number of gates in the encoder and decoder
of MS-ECC is much higher than the one in Flexicache which presents higher
overhead in both read/write energies (4th line in the table) and area (5th line in
the table). Both Flexicache and MS-ECC require changes in the address decoder
of the cache to be able to write more than one line simultaneously. The overhead
of these address decoders are similar in both schemes.
Energy Reduction:
Figure 6 presents the energy consumption of cache op-
erations (i.e. read/write energy and static energy). For read and write energies,
TMR allocates three cache ways in a non-modified cache which triplicates the
energy consumption. Similarly MS-ECC allocates two cache ways (1 for data and
the other for parity bits) when the supply voltage is lower than 700 mV, thus at
this point MS-ECC also roughly duplicates reading and writing energies. This is
mainly because the size of the in/out data is duplicated (or triplicated). Also, the
energy consumption of the OLSC decoder is very high (i.e. 50%). Thus, which
diminish the energy saving of scaling voltage for read energy as it can be seen
at 600mV when OLSC is activated in MS-ECC (Figure. 6a and Figure. 6b). On
the other hand, Flexicache accomplishes replication and fault recovery within a
way without increasing the size of the data in/out bus coming to the way. Thus,