Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
E
k
E
θ
E
φ
z
B
o
=
B
y
y
+
B
z
z
θ
k
θ
=
−
y
y
φ
=
x
x
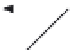
Fig. 12. Coordinate system used for analyzing wave propagation in a magnetized plasma.
The magnetic field
B
o
is on the
yz
-plane and angle
θ
is measured from
B
o
to the propagation
vector
k
which is parallel to the
z
-direction. The wave field
E
has three mutually orthogonal
in directions
k
=
z
,
ˆ
θ
=
−
y
, and
ˆ
φ
=
x
, respectively.
ˆ
components
E
k
,
E
, and
E
φ
θ
is the
θ
k
×
and
ˆ
ˆ
φ
≡
direction of increasing
θ
θ
.
N
e
e
2
/
=
ω
≡
=
Above
k
o
/
c
is the free-space wavenumber,
ω
p
o
m
e
and
Ω
e
eB
o
/
m
e
are
the plasma- and electron gyro-frequencies, respectively, and
θ
is the angle measured from the
magnetic field vector to the propagation direction
k
. Also,
ˆ
and
ˆ
θ
φ
are orthogonal unit vectors
normal to
k
as shown in Figure 12.
Note that
F
O
F
X
=
−
Y
L
as demanded by the orthogonality of O- and X-mode terms in (60).
Y
L
F
X
denotes the axial ratio of elliptically polarized modes in (60), which in
turn can be expressed in matrix notation as
E
F
Y
L
=
−
≡
Thus,
a
ja
−
1
e
−
jk
o
n
X
r
A
O
,
e
−
jk
o
n
O
r
e
−
jk
o
n
X
r
θ
E
φ
=
(64)
jae
−
jk
o
n
O
r
−
A
X
are the transverse field components in
ˆ
and
ˆ
where
E
and
E
θ
φ
directions. Note that
a
can
φ
θ
take values within the range 0
1 and that the limits 0 and 1 correspond to the cases of
linearly and circularly polarized propagation modes. Defining
n
≤ |
a
| ≤
n
O
+
n
X
n
O
−
n
X
≡
and
Δ
n
≡
,
2
2
and considering
E
,
o
and
E
,
o
as the field components at the origin, the propagating electric
φ
θ
field (64) can be recast as
E
θ
E
a
2
e
−
jk
o
Δ
nr
e
jk
o
Δ
nr
E
θ
,
o
E
,
e
−
jk
o
nr
1
a
2
e
jk
o
Δ
nr
+
2
a
sin
(
k
o
Δ
nr
)
=
(65)
a
2
e
−
jk
o
Δ
nr
−
(
)
+
+
2
a
sin
k
o
Δ
nr
φ
φ
,
o
T
where
T
is a propagator matrix that maps the fields at the origin into the fields at a distance
r
. Note that in the case of waves traveling in
k
direction, the same matrix
T
can be used to
propagate the fields from a distance
r
to the origin.
−