Chemistry Reference
In-Depth Information
Probe
Probe
eDHFR
eDHFR
NH
2
Target protein
Target protein
OMe
N
=
O
H
2
N
N
O
H
OMe
scheme 2.27
Labelling of target protein via edHFR fusion.
NH
2
N
N
target protein
OH
N
N
OH
OO
P
N
N
O
O
O
OO
P
O
target protein-PCP fusion
O
OO
O
-
P
O
-
O
-
O
HN
O
HN
Sfp
O
P
O
-
S
O
S
O
-
probe
probe
scheme 2.28
Protein labelling via PPTase-PCP tag.
probe with fast kinetics (association within minutes) and minimal background noise in living mammalian cells. The edHFR
approach can be an alternative for gFP for protein labelling with a few benefits, such as smaller size of edHFR (~18 kda),
and easier modification of spectral properties of imaging probes. The system has been used to label the fusion proteins with
many different fluorophores, such as fluorescein-based green and red dyes, bodIPy Texas Red [348], far-red photoswitching
Atto-655 [349], two-photon fluorophore bC575 [350], and luminescent terbium probe [351], for various applications including
super-resolution imaging [349] and time-resolved imaging in living cells [351]. Although the dissociation half-life of edHFR-
TMP complexes is over tens of minutes, covalent modification is preferred in imaging approaches such as single-molecule
tracking and pulse-chase labelling. The Cornish and Sheetz groups applied the proximity-induced reactivity in inhibitor design
and rendered the covalent bond formation between edHFR fusion protein and TMP probe by installing a Cys residue on
edHFR in the contacting position with an arylamide modified TMP probe [352].
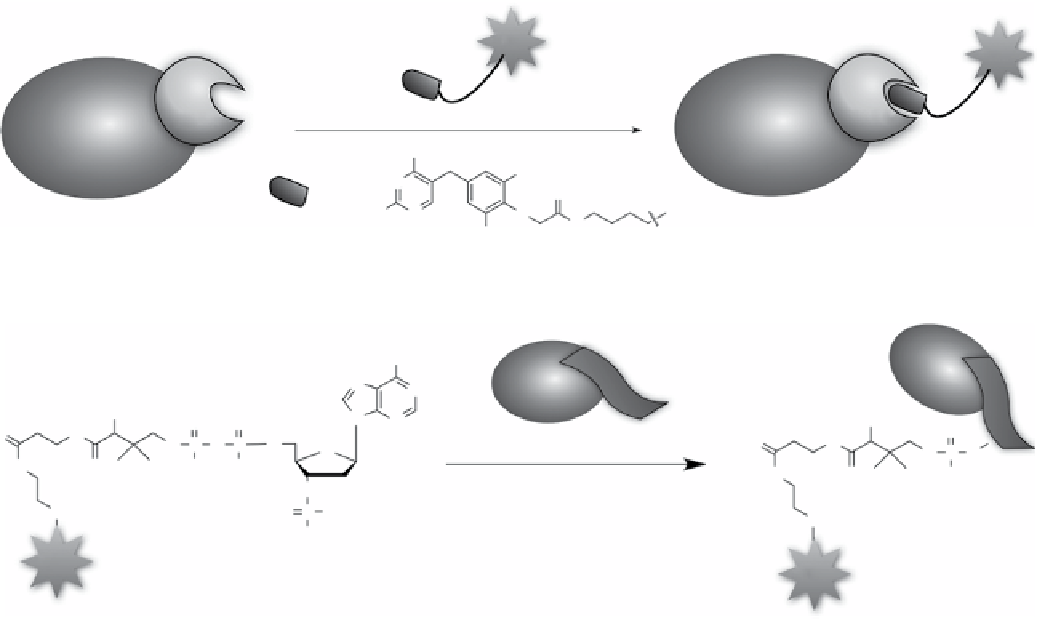
PPTase-PCP Tag
Walsh and co-workers found that a post-translational modification enzyme, phosphopantetheinyl trans-
ferase (PPTase, Sfp) could catalyse the covalent modification of a target protein fused to a peptide carrier protein (PCP)
moiety, excised from nonribosomal peptide synthetase, by a phosphopantetheinyl-modified small molecule (Scheme 2.28)
[353]. The labelling of PCP fusion protein by PPTase was highly specific and efficient in cell lysates and was compatible
with various small molecule probes and proteins.
Cutinase Tag
bonasio et al. reported the use of a fugal enzyme cutinase as a protein tag to label integrin lymphocyte
function-associated antigen-1 on the surface of living cells, whilst not interfering with the conformation or function of the
integrin [354]. Various imaging probes, including quantum dots, could be introduced to the target protein covalently via a
catalysed reaction of p-nitrophenyl phosphonate-conjugates by cutinase.
β-Lactamase
E166N
TEM Tag
β-Lactamases are small bacterial enzymes that hydrolyze β-lactam structures that have been seen
as reporter enzymes for gene expression in mammalian cells [355, 356], as diagnostic and therapeutic targets of bacterial infec-
tion [357-360], as well as in prodrug activation [361]. A mutant of β-lactamase TeM-1,
e166n
TeM, was found to accumulate the
enzyme-substrate intermediate with very slow regeneration of the enzyme. utilising this property of
e166n
TeM, Mizukami et al.
demonstrated fusion protein between epidermal growth factor receptor (egFR), and
e166n
TeM could be labelled specifically
and covalently by β-lactam probes, which were either β-lactam-dye conjugate or β-lactam bridged dye-quencher system [362].